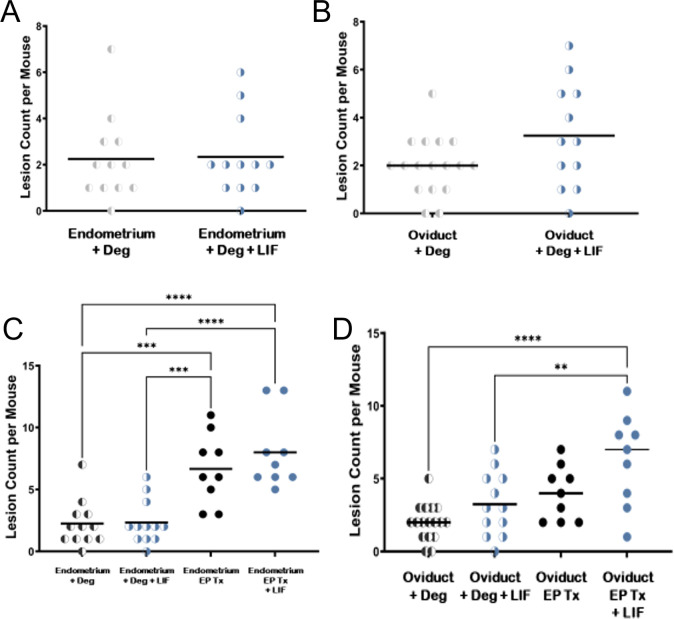
Fig 5. Effects of LIF on ectopic lesion growth.
A. The addition of LIF does not alter the number of endometrial lesions. When the donor and recipient male mice were hormonally suppressed with degarelix, the co-injection of LIF did not demonstrate any statistically significant change in endometrial lesion/mouse compared to solely implanted endometrial controls. B. Addition of LIF alone does not statistically alter the number of oviductal lesions. In hormonally suppressed donor and recipient male mice with degarelix, the co-injection of LIF did not demonstrate significant change in oviductal lesion/mouse compared to solely implanted oviductal controls treated with degarelix. C. Disruption of the estrus cycle by degarelix injection in donor mice significantly reduces the number of endometrial lesions/mouse in comparison with hormonally synchronized controls injected with endometrium (***p<0.001). Addition of exogenous LIF to hormonally synchronized endometrium further significantly increases the number of injected ectopic endometrial lesions/mouse (****P<0.0001). D Implantation of oviductal tissue from hormonally synchronized mice with LIF significantly increases the number of lesions/mouse compared to oviductal lesion number in degarelix treated mice ± LIF (**p<0.01) and hormonally synchronized mice without LIF. E:estrogen, P: progesterone.