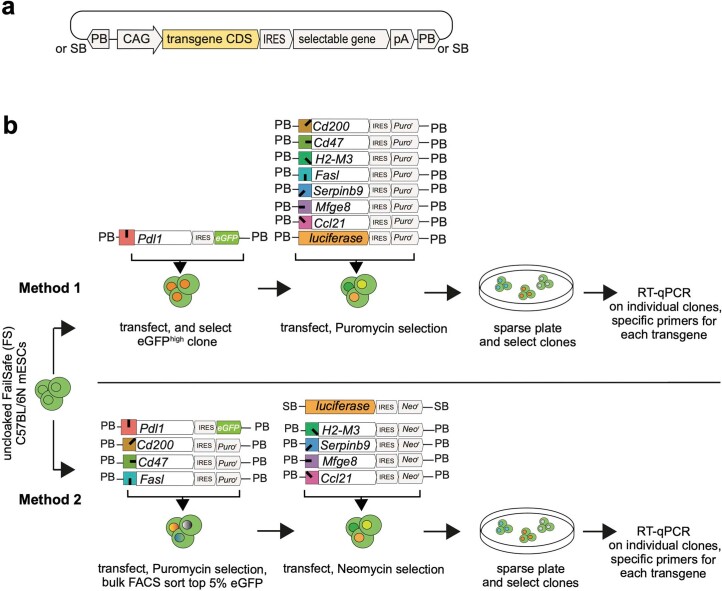
Extended Data Fig. 1. Approach to insert immunomodulatory transgenes into mESCs.
a. Structure of representative piggyBac (PB) or Sleeping Beauty (SB) plasmids used to express the CDS of eight immunomodulatory genes (Ccl21, Pdl1, Fasl, Serpinb9, H2-M3, Cd47, Cd200, and Mfge8) and luciferase in FailSafe B6 mESCs. Gene expression driven by a CAG promoter and linked by an IRES to an eGFP fluorophore, or Puromycin or Neomycin resistance genes. The entire expression cassette is flanked by inverted terminal repeat of piggyBac or Sleeping Beauty transposons. The NCBI Refseq protein ID encoded by each gene CDS is listed in Supplementary Table 1. b. Method 1) Failsafe B6 mESCs were transfected with a PB plasmid encoding an eGFP-linked Pdl1, then a clone with high eGFPhigh expression was isolated. This was followed by co-transfection of PB transposon plasmids encoding Ccl21, Fasl, Serpinb9, H2-M3, Cd47, Cd200, Mfge8 and luciferase and then drug selection with Puromycin. Method 2) FailSafe B6 mESCs were simultaneously transfected with PB plasmids encoding Pdl1, Fasl, Cd47, and Cd200, followed by drug selection with Puromycin and then a FACS sort on clones with high expression of each factor based on antibody staining and and eGFP for Pdl1. Bulk sorted cells then transfected with SB transposons encoding Ccl21, Mfge8, SerpbinB9, H2-M3 and luciferase, followed by drug selection with G418. Both methods resulted in a polyclonal pool that were used to establish clonal lines and analyzed by RT-qPCR for transgene expression levels.