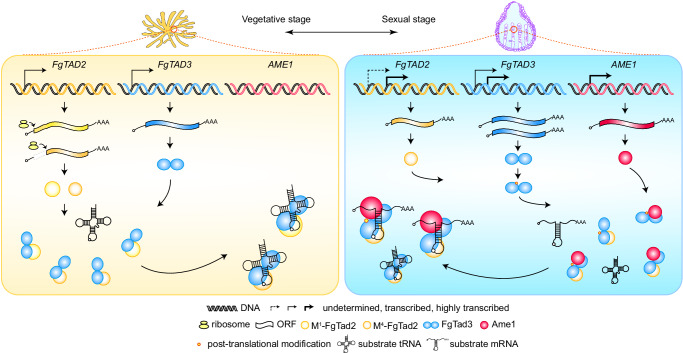
Fig. 8. Proposed models for components, expression, and regulation of A-to-I mRNA editing machinery in F. graminearum.
FgTAD2 encodes proteins that contain a CDA domain, while FgTAD3 encodes proteins that contain both an N-terminal RNA-binding domain and a C-terminal CDA domain. FgTad2 interacts with the CDA domain of FgTad3 to form the catalytic domain responsible for A-to-I editing of both tRNAs and mRNAs. During vegetative stages, FgTAD2 expresses two protein isoforms: M1-FgTad2 and M4-FgTad2, via alternative translational initiation. Compared to M1-FgTad2, M4-FgTad2 has a stronger interaction with FgTad3. In sexual stages, both FgTAD2 and FgTAD3 generate a short transcript isoform via alternative transcriptional initiation in fertile tissues. The long transcript isoform of FgTAD3 is also expressed in fertile tissues, while that of FgTAD2 remains to be determined. The short transcript isoform of FgTAD2 encodes proteins identical to M4-FgTad2, while both transcript isoforms of FgTAD3 encode the same proteins. A gene named AME1 (activator of mRNA editing) is induced to expression in sexual stages, which encodes proteins with a DUF726 domain. Ame1 interacts with the N-terminal domain of FgTad3 to mediate the recognition of mRNA substrates. The FgTad2-FgTad3-Ame1 complex performs A-to-I mRNA editing. FgTad3 also undergoes post-translational modification that is important for mRNA editing.