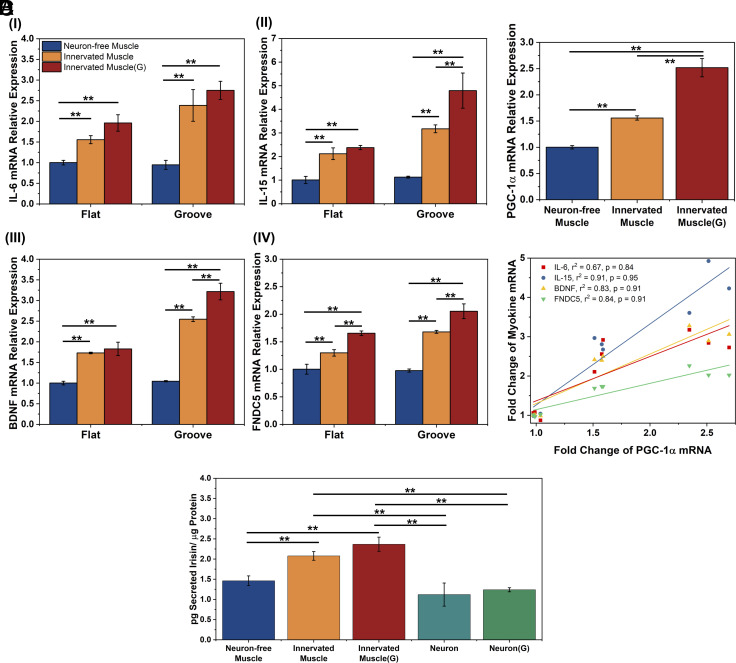
Fig. 4.
Effect of neuronal innervation on myokine-encoding mRNA expression and irisin secretion of skeletal muscles. Primary myoblasts were used in this analysis. (A) IL-6 (I), IL-15 (II), BDNF (III), and FNDC5 (IV)-encoding mRNA levels of Neuron-free Muscle, Innervated Muscle, and Innervated Muscle(G) on the flat and the microgrooved substrates after 8 d of coculture. mRNA levels were quantified with a fold change to the expression of Neuron-free Muscle formed on the flat substrate. (B) PGC-1α-encoding mRNA expression of muscles on the grooved substrate. (C) Correlation of IL-6, IL-15, BDNF, and FNDC5-encoding mRNA expressions to PGC-1α-encoding mRNA expression of the muscles on the grooved substrates. (r2: R-squared value, p: correlation coefficient) (D) Extracellular irisin concentration normalized to the total intracellular protein level of muscles or NSC-derived neurons (Neuron) and NSC-derived neurons incubated with 500 µM glutamate [Neuron(G)] on the microgrooved substrate. The protein concentration was measured after 8 d of coculture (n = 3, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01).