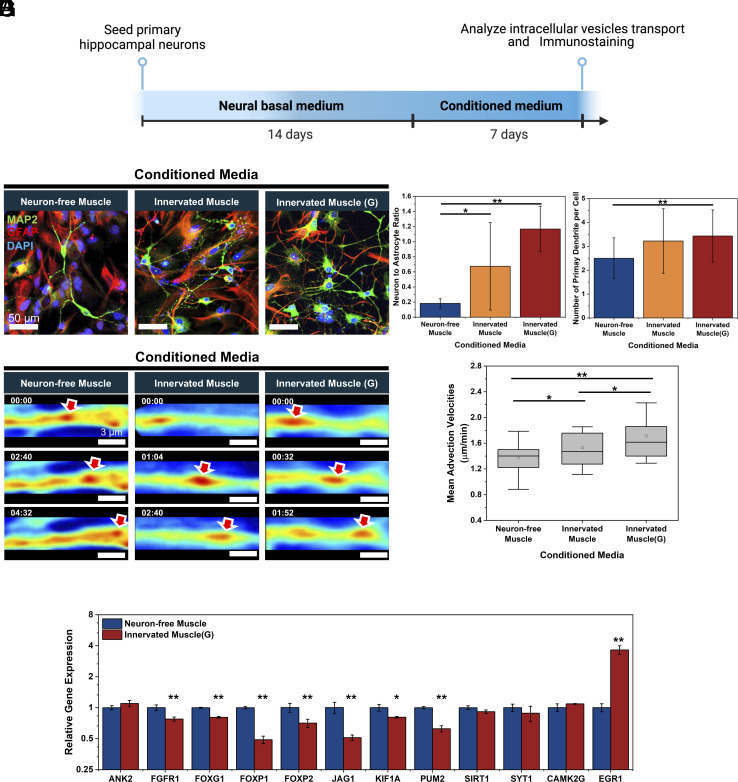
Fig. 6.
Effects of muscle-derived conditioned media on neural development and intracellular axon transport. (A) Timeline of testing effects of muscle-derived conditioned media on hippocampal neurogenesis. Three different conditioned media were harvested from Neuron-free Muscle, Innervated Muscle, and Innervated Muscle(G) cultured on the microgrooved substrate. (B) Immunofluorescence images of hippocampal neurons cultured with conditioned media for 7 d. [neurons (MAP2, green), astrocytes (GFAP, red), and nuclei (DAPI, blue)] (C) Neuron-to-astrocyte ratio and (D) number of primary dendrites per cell altered with three different conditioned media (n > 5 per group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). (E) Representative SLIM-based images of vesicular transport in neurites incubated with conditioned media (minutes:seconds). Red arrows indicated the tracked vesicles. (F) Mean advection velocities of vesicles transported in neurites quantified from SLIM images (n > 40 neurites, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). (G) Comparative gene expression analysis in hippocampal neurons after 7 d culture with conditioned media from Innervated Muscle(G) versus Neuron-free Muscle (n = 3, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01).