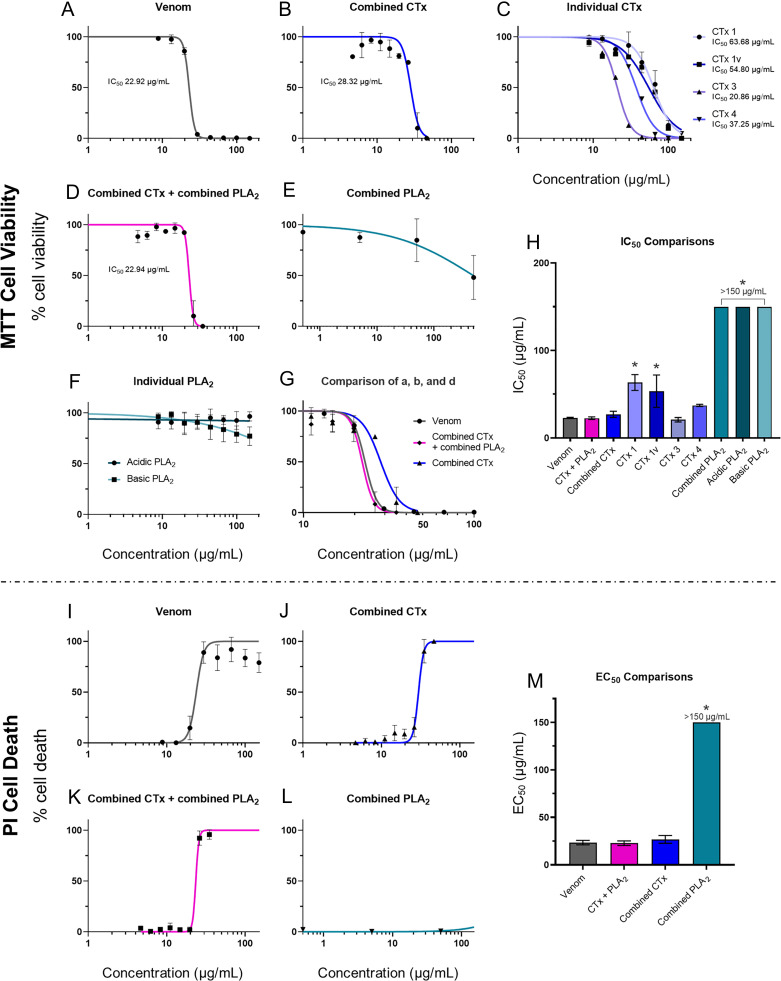
Fig. 2.
Crude venom and purified CTx inhibit cell viability, with CTx venom activity modestly potentiated by PLA2 toxins. Cell viability was measured in immortalized human keratinocytes (HaCaT cells) using MTT assays (A–H) and multiplexed with PI assays to measure cell death (I–M). HaCaT cells were treated for 24 h with serial dilutions of East African (Tanzania) N. nigricollis venom or its isolated toxins. MTT concentration–response curves are shown for (A) crude East African N. nigricollis venom, (B) combined purified CTx, (C) individual purified CTx, (D) combined CTx and combined PLA2 together, (E) combined purified PLA2, and (F) individual purified PLA2. (G) Direct comparison of the concentration–response curves caused by crude venom, combined CTx, and the combined CTx + combined PLA2 together. Note the different scale on the x-axis in comparison with panels A–F. (H) IC50 value summary of the various venom toxins displayed in (A–F) using MTT assays. PI concentration–response curves are shown for (I) crude N. nigricollis venom, (J) combined purified CTx, (K) combined CTx and combined PLA2 together, and (L) combined purified PLA2. (M) EC50 values of the various venom toxins displayed in (I–L) using PI assays. For panels A–F, the data shown represent mean % cell viability and corresponding SDs. For panels I–L, the data shown represent mean % cell death and corresponding SDs. All data displayed are from three independent experiments with each condition conducted in triplicate. Data were normalized to 0 to 100% between the lowest and highest read values for analysis, then plotted as concentration–response curves using GraphPad Prism 9. For panels H and M, statistically significant differences determined by one-way ANOVAs with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons post hoc tests are denoted by asterisks: *P < 0.05.