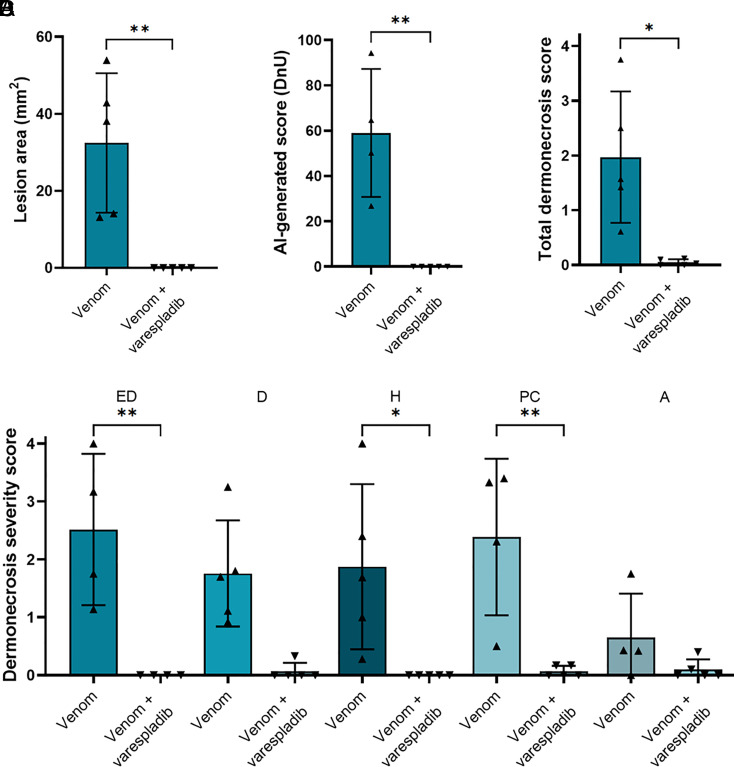
Fig. 5.
Dermonecrosis caused by N. pallida venom is prevented by the PLA2 inhibitor varespladib. Groups of mice (n = 5) were intradermally injected with 25 µg N. pallida venom with or without the PLA2 inhibiting drug varespladib (19 μg). At 72 h postinjection, lesions were excised and examined, from which it was determined that the PLA2 inhibitor varespladib significantly reduced the size and severity of the dermonecrotic lesions caused by N. pallida venom as measured with (A) calipers, (B) VIDAL, and (C) histopathological analysis of the (D) different skin layers (ED, epidermis; D, dermis; H, hypodermis; PC, panniculus carnosus; A, adventitia). For (C and D), the data shown represent the total mean dermonecrosis score of all layers, vs. the mean damage score for each individual skin layer, respectively, and corresponding SDs. Statistically significant differences were determined by unpaired t test comparisons for (A–C), and by two-way ANOVA, followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons tests for (D). Statistically significant differences are denoted by asterisks: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. Error bars represent SDs.