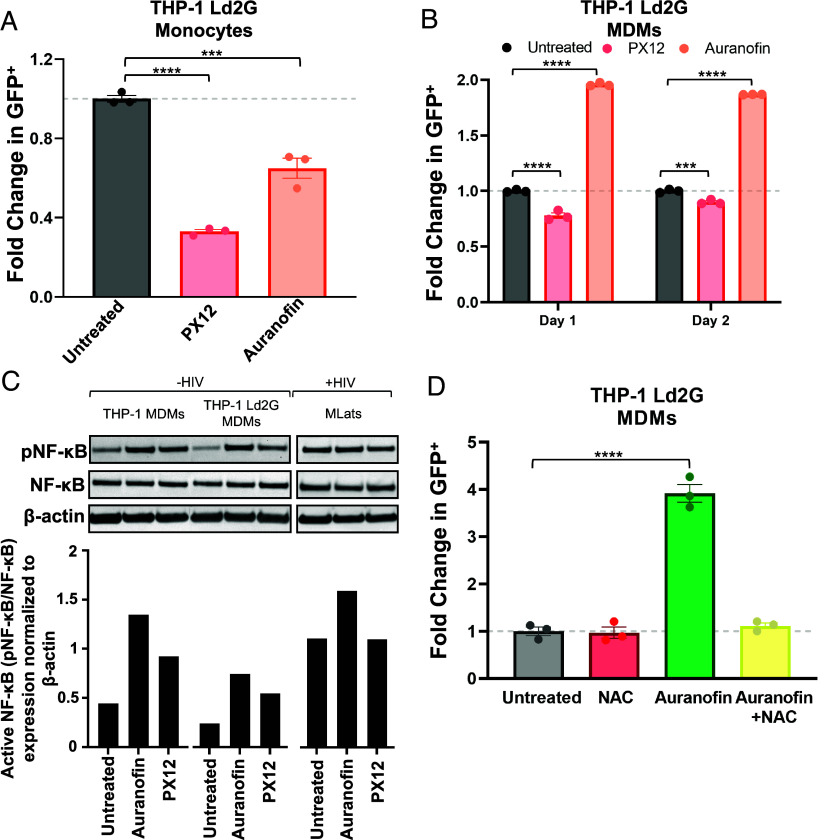
Fig. 6.
Auranofin induces NF-κB activation of the HIV LTR promoter. (A) TNF-a alone or in combination with 4 µM Auranofin or 60 µM PX12 was added to THP-1 Ld2G monocytes for 24 h to evaluate LTR promoter activity. Statistical significance was determined by performing a one-way ANOVA comparison with Dunnett correction (***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001). (B) Auranofin or PX12 were added to THP-1 Ld2G MDMs at day 0 postdifferentiation for 24 h and 48 h to evaluate LTR promoter activity. Statistical significance was determined by performing a two-way ANOVA comparison with Dunnett correction (***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001). (C) Western blot analysis of phosphorylated NF-κB (pNF-κB), total NF-κB, and B-actin (housekeeping) in THP-1 (uninfected) MDMs, THP-1 Ld2G (minimal HIV promoter circuit) MDMs, and MLats (latently infected) at day 1 postdifferentiation (Top). Quantification of western blot results was performed by normalizing protein levels to B-actin. The ratio of pNF-κB to NF-κB was used to quantify activated levels of NF-κB, (Bottom). (D) N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC; 10 µM) was added to THP-1 Ld2G MDMs at day 0 postdifferentiation for 1.5 h before the addition of Auranofin. LTR promoter activity was evaluated after 4 h of treatment via flow cytometry. Statistical significance was determined by performing a one-way ANOVA comparison with Dunnett correction (****P < 0.0001). Data points represent three independent replicates ± SEM.