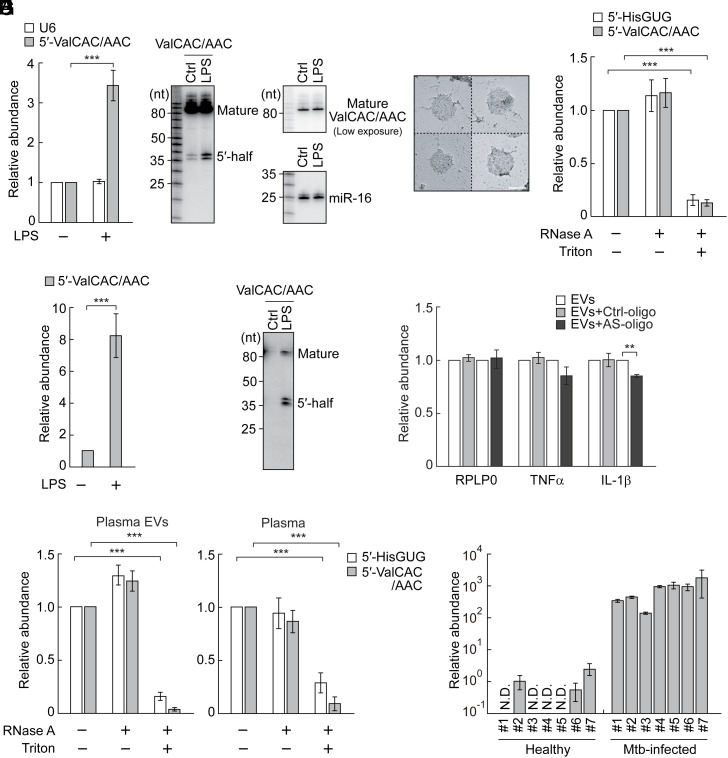
Fig. 2.
Enhanced accumulation of the ex-5′-tRNAValCAC/AAC half in EVs from LPS-treated HMDMs and in plasma from Mtb-infected patients. (A) Total RNAs from HMDMs treated with LPS were subjected to TaqMan RT-qPCR for the 5′-tRNAValCAC/AAC half. U6 snRNA was quantified as a control. The quantified RNA levels were normalized to the levels of 5S rRNA. (B) Total RNAs from HMDMs treated with LPS were subjected to northern blot for the 5′-tRNAValCAC/AAC half and its corresponding mature tRNA. miR-16 was analyzed as a control. (C) Transmission electron microscopic evaluation of the isolated EVs. Four representative EV images are shown. (Scale bar, 100 nm.) (D) HMDM-secreted EVs were treated with RNase A and/or Triton X-100 and then subjected to TaqMan RT-qPCR for quantification of 5′-tRNA halves. (E and F) Total RNAs from HMDM-secreted EVs were subjected to TaqMan RT-qPCR (E) and northern blot (F) for the 5′-tRNAValCAC/AAC half. (G) EVs from LPS-treated HMDMs were mixed with DOTAP-fused AS-oligo of the 5′-tRNAValCAC/AAC half or Ctrl-oligo with scrambled sequences and applied to recipient HMDMs, followed by quantification of the indicated mRNAs. (H) Human plasma and its isolated EVs were treated with RNase A and/or Triton X-100 and then subjected to TaqMan RT-qPCR for quantification of 5′-tRNA halves. (I) RNAs isolated from plasma samples of healthy individuals or Mtb-infected patients were subjected to TaqMan RT-qPCR for the 5′-tRNAValCAC/AAC half. The quantified 5′-tRNA half levels were normalized to spike-in RNA levels. The relative abundances to the healthy sample #2 (set as 1) are shown.