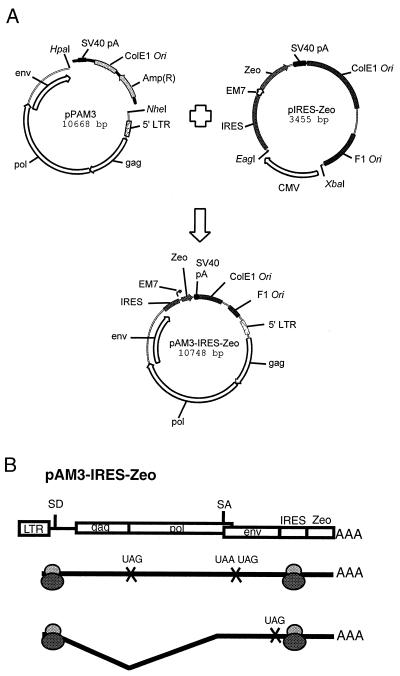
FIG. 1.
Construction and cap-independent translation mechanism of the chimeric pAM3-IRES-Zeo helper virus. (A) Plasmids used in this study. For details of their construction, see Materials and Methods. Briefly, a 2.8-kb fragment including the IRES-Zeo expression cassette, an SV40 polyadenylation signal sequence, the bacterial replication origin (ColE1 Ori), and phage replication origin (F1 Ori) was excised from pIRES-Zeo. The ColE1 Ori and ampicillin resistance gene (Ampr) of pPAM3 were replaced with the above 2.8-kb IRES-Zeo-containing fragment from pIRES-Zeo. The EM7 prokaryotic promoter located at the 5′ end of the Zeo gene permits selection for pAM3-IRES-Zeo in bacteria. (B) Genomic RNA of MoMLV contains two internal stop codons at the 3′ ends of the gag and pol genes that terminate cap-dependent translation and allow appropriate ratios of viral structural proteins. In pAM3-IRES-Zeo-derived transcripts, ribosomes also recognize the IRES sequence and initiate translation from the first AUG codon of Zeo downstream of the IRES sequence. A portion of genomic RNA is spliced into env transcripts that are translated in a cap-dependent mechanism. SD, splicing donor; SA, splicing acceptor.