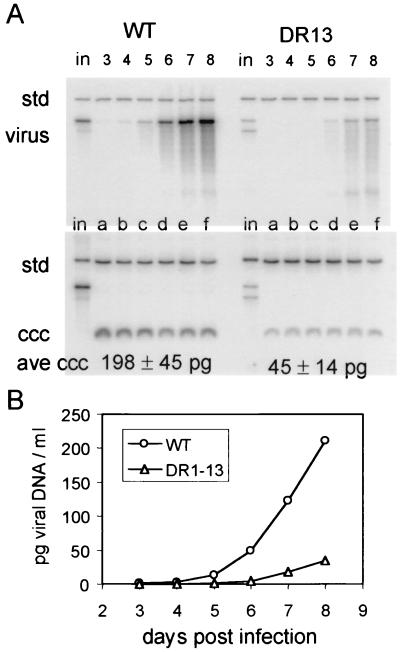
FIG. 6.
cccDNA and extracellular virus production by DR1-13- or wild-type-infected PDHs. PDH cultures were infected for 24 h with approximately 108 viral genomes of DHBV and incubated with daily medium changes. At the end of 8 days, the cultures were harvested, and cccDNA was extracted. The DNA for enveloped virus particles was extracted from each day's medium. (A) Viral DNAs were mixed with 300 pg of linearized DNA from plasmid pSPDHBV5.1(2X), containing a head-to-tail dimer of the DHBV genome (std), and assayed for viral DNA by agarose gel electrophoresis and blot hybridization. Viral DNA extracted from the 24-h culture medium at the indicated days for wild-type- and DR1-13-infected cells (virus) is seen in the top panel, and cccDNA extracted at 8 days postinfection (ccc) is shown in the bottom panel. The viral DNA yields were calculated by comparison of the viral DNA bands to the internal standard bands by phosphorimage analysis. Samples equivalent in the inoculum (in) of each plate of PDHs were run in each analysis. Each cccDNA sample is that obtained from one 60-mm plate of PDHs, and each viral DNA sample loaded was that obtained from a 16-ml 24-h culture medium (four plates of PDHs). The mean value for the amount of cccDNA per each plate is indicated at the bottom of panel A. (B) DNA from enveloped virus particles in the culture medium over 8 days postinfection is plotted as the cumulative total DNA per milliliter (4 ml per plate). The final slope of the curve indicates the rate of virus release for wild-type- or DR1-13-infected cells. The calculated relative rate of virus release of DR1-13-infected cells, normalized to that of cccDNA, 0.69.