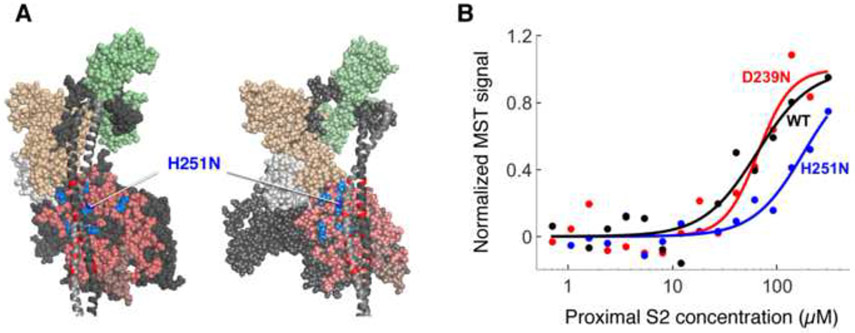
Figure 4.
Binding of H251N and D239N human β-cardiac sS1s to human cardiac proximal S2. (a) Structural model of homology-modeled sequestered heads of human β-cardiac S1 based on the 3D-reconstructed structure of tarantula skeletal muscle myosin thick filaments (Alamo et al., 2008). A short version of myosin HMM, showing only 126 residues of the coiled-coil S2 domain, is illustrated in two projections. The heavy chain residues of the S1 head on the left are colored pink (mesa residues), dark blue (H251N), light blue (arginine HCM mutations), white (the converter domain), and dark grey (all remaining residues). The ELC is colored light brown and the RLC is light green. HCM-causing mutations of glutamate and aspartate residues in the proximal S2 tail are shown in red. H251N is at the interaction site of S1 and S2, while D239N is remote from this site and not visible in this projection (b) Representative MST binding curves (fit to the Hill Equation) of WT and mutant human β-cardiac sS1s tagged with a C-terminal eGFP to human proximal S2 give the affinity of the sS1 to S2 (KD)