Figure 1. Glycolytic pathway.
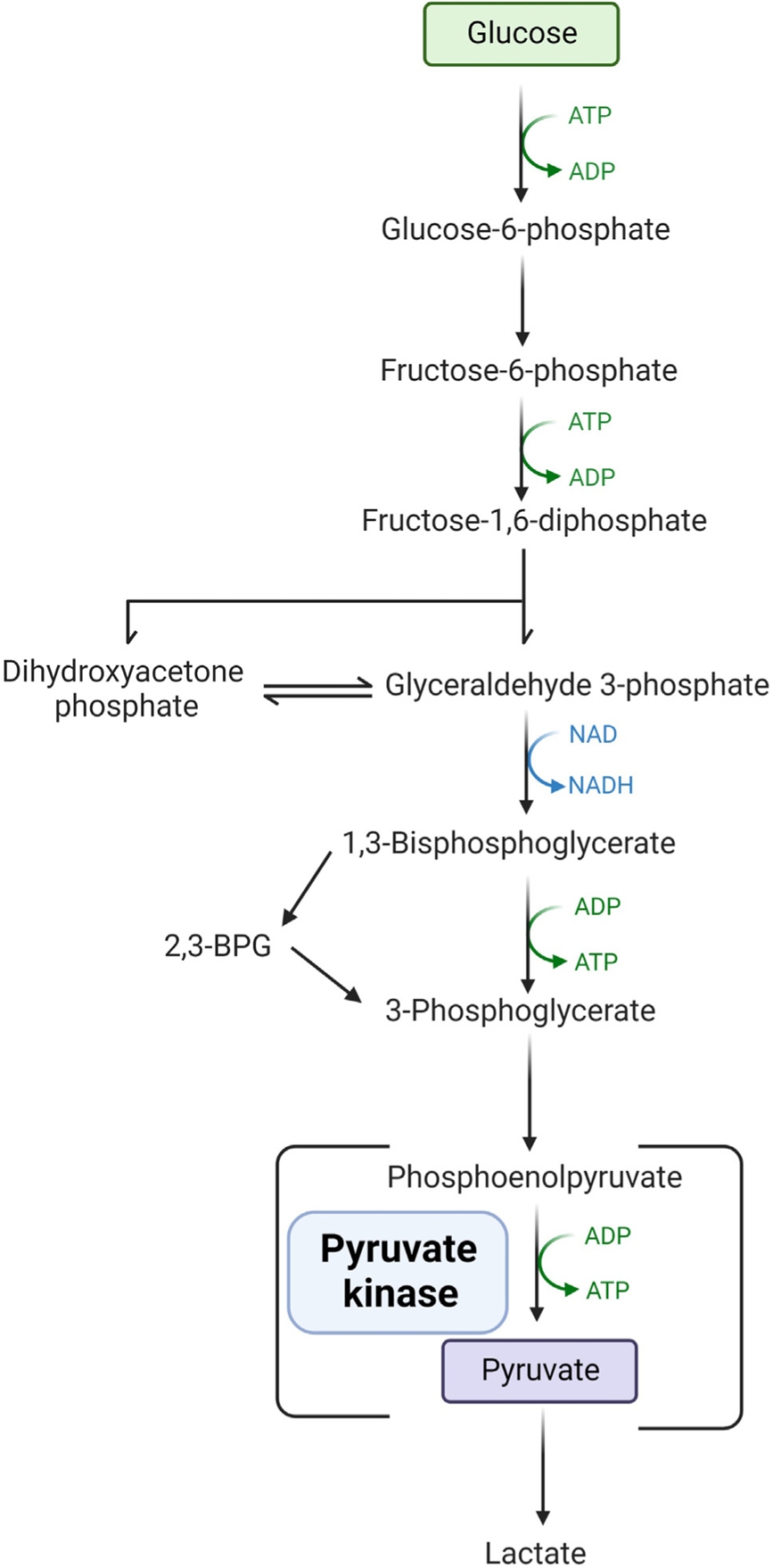
Mature red blood cells lack a nucleus and mitochondria and rely on glycolysis for the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Pyruvate kinase is an enzyme in the terminal part of the pathway converting phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate with the production of ATP. With a deficiency of pyruvate kinase, the production of proximal byproducts, such as 2–3-biphosphoglycerate (2,3-BPG), is increased. Abbreviations: ADP: adenosine diphosphate; NAD: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NADPH: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate.
