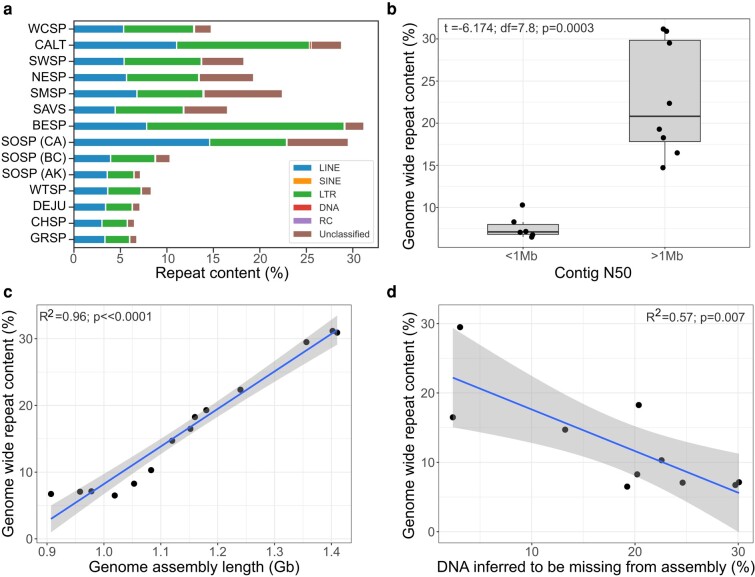
Fig. 3.
a) Percentage of the genome comprising interspersed repeats, including: retroelements (LINE, SINE, LTR), DNA transposons (DNA), rolling-circles (RC), and unclassified elements (white-crowned sparrow, WCSP; California towhee, CALT; swamp sparrow, SWSP; Nelson's sparrow, NESP; saltmarsh sparrow short-read, SALS_SR; saltmarsh sparrow long-read, SALS_VG; Savannah sparrow, SAVS; Bell's sparrow, BESP; song sparrow, SOSP; white-throated sparrow, WTSP; dark-eyed junco, DEJU; chipping sparrow, CHSP; grasshopper sparrow, GRSP). b) The relationship between contig N50 and genome-wide repeat content. Significantly higher levels of repeat content were discovered in genomes with a contig N50 greater than 1 Mb. All of which were generated with PacBio long-read technology. c) Correlation between percent repeat content identified in each genome and the length of the assembled genome in Gb. d) Correlation between percent repeat content and the amount of DNA inferred to be missing from each of the sparrow assemblies. C-value is assumed to be the more accurate estimate of total genome length. Percent missing DNA from each sparrow assembly is estimated as the difference between the c-value and assembly length.