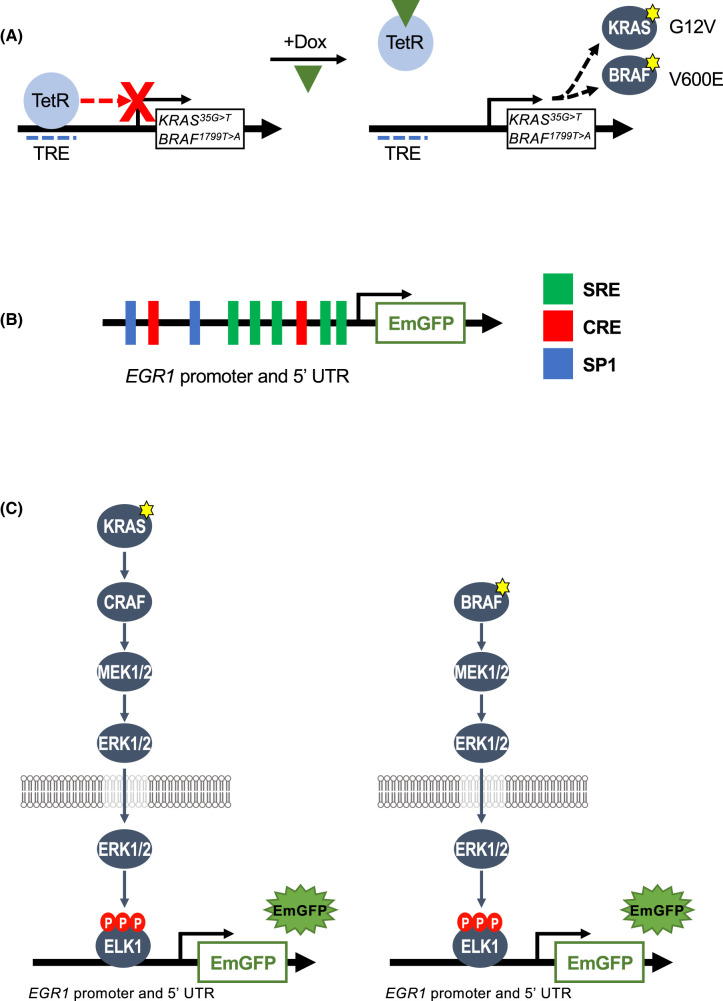
Figure 1. Components of KRASG12V- or BRAFV600E-driven ERK1/2-dependent EmGFP reporter.
(A) Schematic of the doxycycline-inducible Tet Repressor (TetR) system used in this study. HeLa cells were engineered to express either KRAS35G>T (encoding KRASG12V) or BRAF1799T>A (encoding BRAFV600E) under the control of tetracycline response element (TRE). In the absence of doxycycline (Dox) TetR binds the TRE and inhibits transcription. Binding of Dox to the Tet causes it to dissociate from the TRE, allowing transcription of KRAS35G>T or BRAF1799T>A. (B) The promoter region and 5′UTR of EGR1 (−778 to +280), inserted upstream of the EmGFP cDNA. The promoter consists of five critical ERK1/2 responsive serum-response elements (SREs), as well as two cAMP-responsive elements (CREs) and two SP1 elements. (C) HeLa TetR KRASG12V cells (left) or HeLa TetR BRAFV600E cells (right) have been engineered to express an EGR1:EmGFP reporter construct. Treatment of these clones with Dox should drive expression of KRASG12V or BRAFV600E, leading to activation and nuclear entry of ERK1/2 which then phosphorylates and activates ELK1 which in turns drives transcription of EmGFP from the EGR1 promoter and 5′UTR.