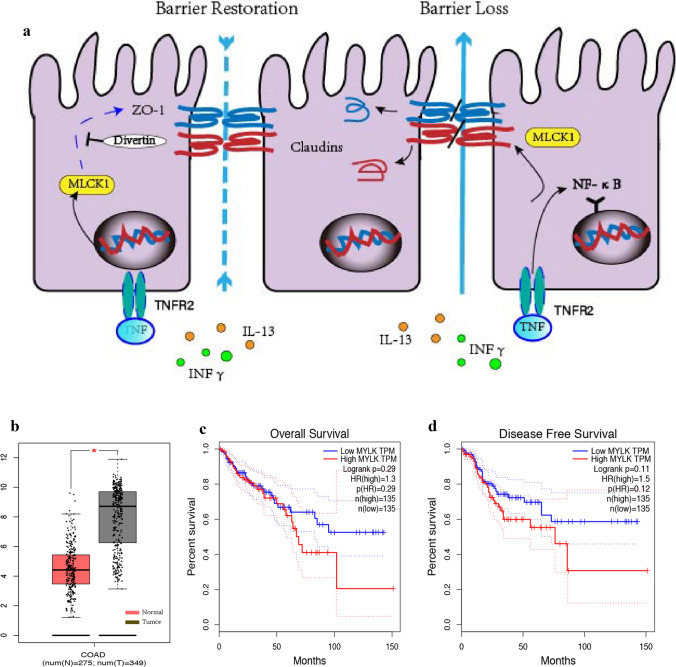
Fig.1.
Mechanism of action of MLCK1 and analysis of data from TCGA. a recruitment of MLCK1 to the perijunctional actomyosin ring (PAMR) affects the binding of tight junction-related proteins such as ZO-1, claudins, and then increases the permeability of epithelial tight junctions, thereby causing a reduction in intestinal barrier function. A small molecule named Divertin that MLCK1 recruitment to the PAMR, restores barrier function and prevents disease progression in experimental inflammatory bowel disease caused by pro-inflammatory cytokine such as TNF, INF and et.al. b analysis of data from TCGA showed a significant difference in MLCK1 expression between normal and colorectal cancer patients (p < 0.01). c, d no significant correlation with overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS)