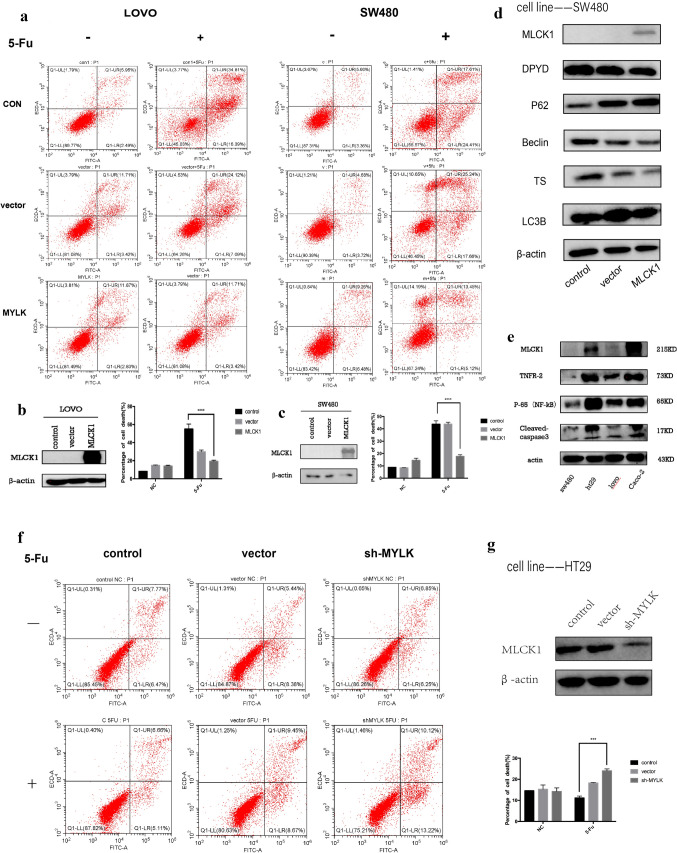
Fig.3.
Transient overexpression of MLCK1 and knockdown expression of MLCK1. a–c after plasmid transfection of two screened low-expressing MLCK1 cell lines (LOVO and SW480) overexpressing MLCK1, and treated them with different concentrations of 5-Fu (200ug/ml in LOVO cell line and 400ug/ml in SW480 cell line) for 24h, cell death in control and dosing groups was detected using flow apoptosis, and the results suggested that for LOVO and SW480 cell lines, colon cancer cells were significantly less sensitive and more resistant to 5-Fu after overexpressing MLCK1, the p < 0.05, statistically significant difference. f, g the sensitivity of HT29 colon cancer cells to 5-Fu was significantly increased after knocking down the expression of MLCK1(sh-MYLK), and the flow cytometry results after 5-Fu adding suggested higher cell mortality, p < 0.05, statistically significant difference. d for SW480 cell line, the expression levels of autophagy-related proteins, i.e., LC3B II and Beclin-1 decreased and P62 increased after plasmid transfection with high expression of MLCK1, suggesting a decrease in death autophagy levels. e results of western blot after protein extraction of the four cell lines selected in the primary screen suggested that TNFR2 and NF-κB (P65) protein expression was higher in cell lines with higher expression of MLCK1 (HT29, CACO2) and lower in cell lines with lower expression of MLCK1 (LOVO and SW480)