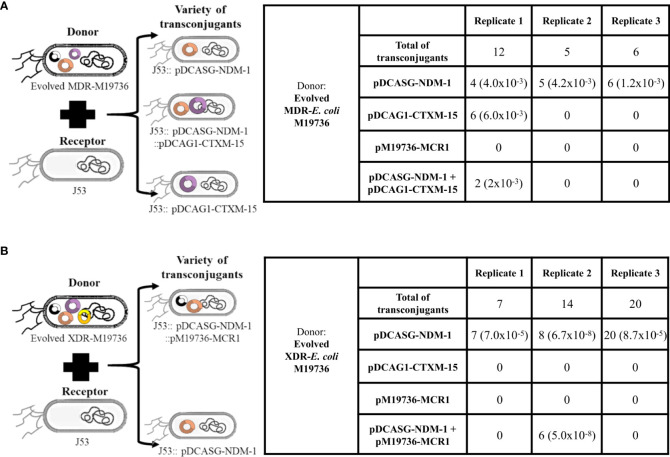
Figure 4.
Dissemination of plasmids co-infecting evolved Escherichia coli M19736 strains to E. coli J53. Evolved MDR-E. coli M19736 and XDR-E. coli M19736 were tested as donors of co-infecting clinical conjugative plasmids using as receptor E. coli J53 (A, B). The selection was performed with 8 µg/ml of ceftazidime. The number of colonies detected with each gene (bla NDM-1, bla CTX-M-15, and/or mcr-1) in transconjugants is shown. Numbers in parentheses represent the conjugation efficiencies of each experiment for the plasmids. Conjugation efficiencies were calculated as the quotient between the number of transconjugants (Tc) and the number of donors (D) (Tc/D). Both evolved strains were able to transfer the bla NDM-1 gene located in pDCASG-NDM-1 to E. coli J53 from three independent biological replicates. When the evolved MDR-E. coli M19736 was used as donor, two other genotypes were identified in transconjugants in one replicate (A). The first genotype harbored simultaneously plasmids of the bla NDM-1 (pDCASG-NDM-1) and bla CTX-M-15 (pDCAG1-CTX-M-15) genes in E. coli J53 transconjugants. The second one harbored only the bla CTX-M-15 (pDCAG1-CTX-M-15) gene. When the evolved XDR-E. coli M19736 was used as donor, in one replicate, another genotype was identified in which the bla NDM-1 (pDCASG-NDM-1) and mcr-1 (pM19736-MCR-1) genes were detected simultaneously (B).