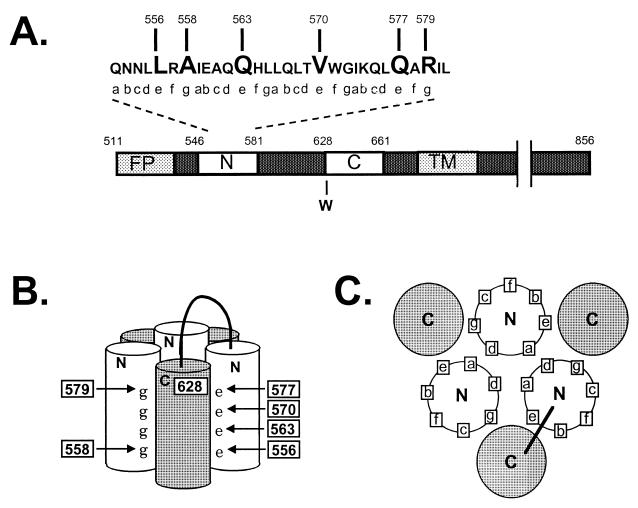
FIG. 1.
Diagram of the gp41 self-assembly domain. (A) Linear representation of domains in gp41. FP, fusion peptide; N, heptad repeat motif located near the fusion peptide, containing sequences from DP-107 and N36; C, heptad repeat motif located near the transmembrane domain (TM) containing sequences from inhibitory C peptides (9, 11; C. Wild, T. Greenwell, and T. Matthews, Letter, AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 9:1051–1053, 1993). Numbering corresponds to amino acid from the HXB2 clone of HIV-1 (Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, N. Mex.). (B) Schematic representation of the self-assembly domain. N and C, heptad repeat regions that self-assemble to form the six-helix bundle structure (hairpin structure). e and g, positions of residues in the heptad repeat motif. Numbers indicate the positions of mutations. A loop connects the N and C helices from a gp41 monomer. The numbering is as described above and shows the antiparallel orientation of the N and C helices. (C) A cross-sectional view of the self-assembly domain, looking down from the connecting loop region, shows the orientation of heptad repeat residues.