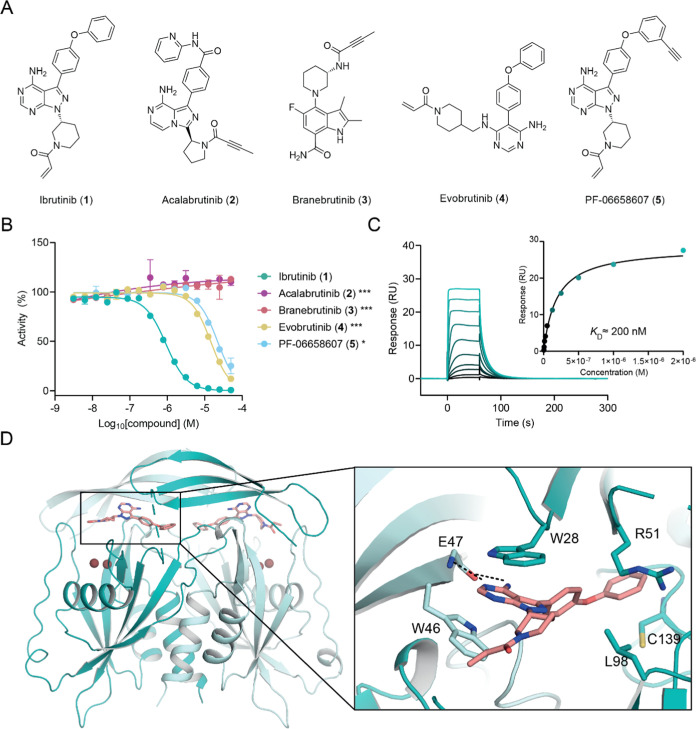
Figure 1.
Identification and validation of ibrutinib (1) as a noncovalent NUDT5 inhibitor. (A) Chemical structures of BTK inhibitors. (B) NUDT5 catalytic activity assay results (1: IC50 = 0.837 ± 0.329 μM, 4: IC50 = 13.9 ± 0.6 μM, 5: IC50 = 21.2 ± 1.0 μM). Data are shown as mean ± standard deviation (SD) and are based on three technical replicates. Graph is representative of two independent biological replicates (n = 2). Stars indicate Student’s t test p-value comparing compound activity at the highest concentration against 1 (* < 0.05, *** < 0.001). (C) SPR sensorgram showing binding of 1 to NUDT5 (KD ≈ 200 nM). (D) Crystal structure of ibrutinib (1) bound to NUDT5 (PDB: 8RDZ). Compound 1 occupies the active site of the NUDT5 dimer where it mediates π–π stacking interactions with W46 of chain A (teal) and W28 of chain B (pale teal). An additional hydrophobic interaction with R51 in chain B and a hydrogen bond with the main chain of E47 in chain A can be observed. Compound 1 (salmon) and interacting residues are shown in stick representation.