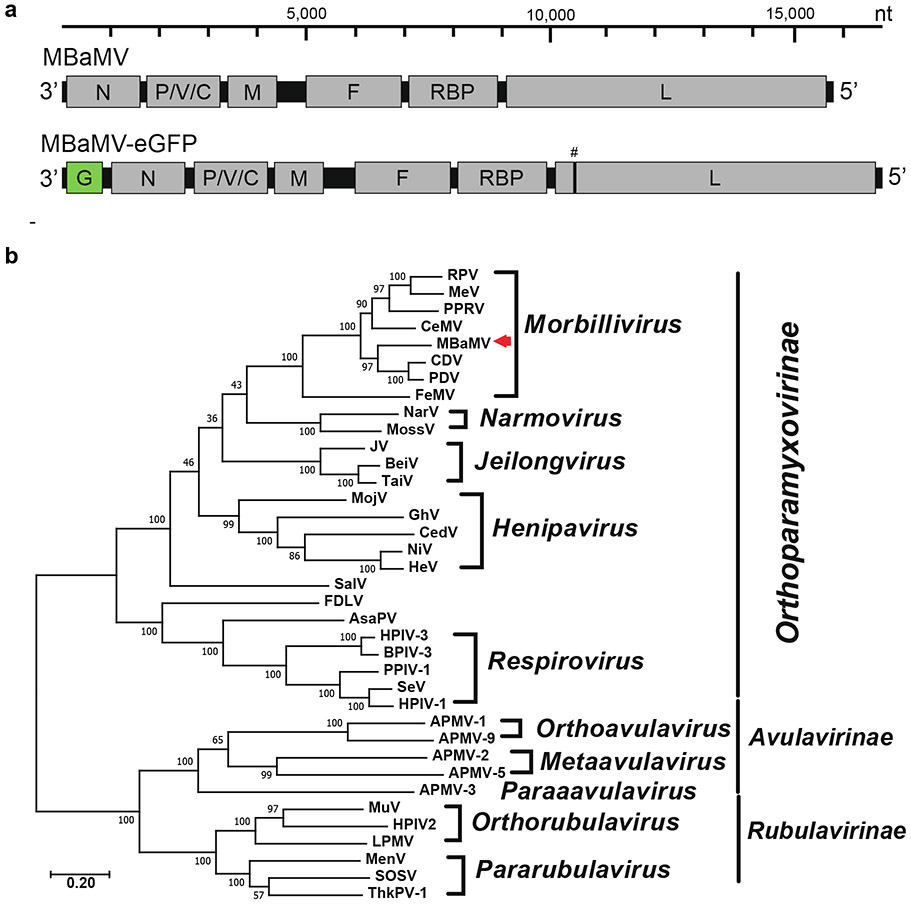
Extended Data Figure S1. The genomic composition of myotis bat morbillivirus (MBaMV) and its phylogeny.
a, Schematic representation of the MBaMV genome and its encoded genes. The recombinant MBaMV-eGFP generated in this study is also shown. eGFP transcriptional unit is depicted as ‘G’ (green box). # indicates the position in L where silent mutations were introduced to prevent expression of putative ORF-X that appeared toxic in bacteria (Extended Data Figure 3). The nucleotide scale bar is provided for context. b, The entire amino acid sequence of the L protein was used for constructing the phylogenetic tree of representative viruses from the three major subfamilies of Paramyxoviridae. L protein sequences were first aligned by clustalw, then the phylogenetic tree was generated by the maximum likelihood method using MEGA 10 (version 10.1.8). The numbers at each node indicate the fidelity by bootstrap test (1,000 times). MBaMV (red arrowhead) was most closely related to canine distemper virus (CDV) and phocine distemper virus (PDV) until the recent discovery of porcine morbillivirus (PoMV). The scale indicates substitutions per site. The accession numbers for the sequences used in this phylogenetic analysis are shown at Extended Data Table 2.