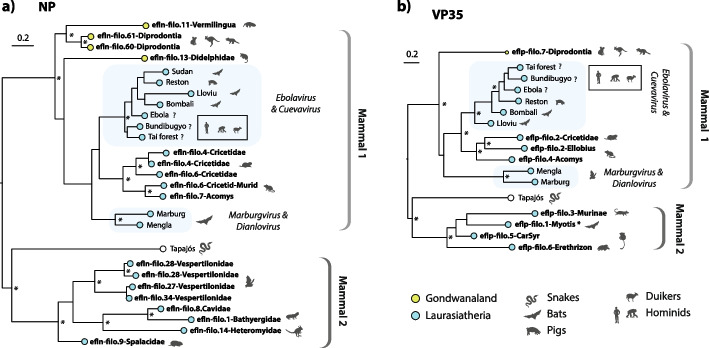
Fig. 5.
Evolutionary relationships of filoviruses and filovirus-derived EVEs. Bootstrapped maximum likelihood phylogenies showing the evolutionary relationships between filoviruses and filovirus EVEs in the nucleoprotein (NP) and viral protein 35 (VP35) genes. Phylogenies were constructed using maximum likelihood as implemented in RAxML, and codon-aligned nucleotides for each gene. Numbers adjacent internal nodes indicate bootstrap support (1000 bootstrap replicates). The scale bar indicates evolutionary distance in substitutions per site. Virus taxon names are shown in regular font, EVE names are shown bold. EVE names follow standardized nomenclature (see “Materials and methods”). Brackets to the right of each tree indicate virus genera (italics) and major lineages (bold). Silhouettes indicate host groups following the key. For Ebola virus, Bundibugyo virus, and Tai Forest virus, the main reservoir hosts are unknown. The inset box adjacent these taxa show host species in which one or more of these viruses has been isolated [81, 82], following the key. *Experimentally investigated locus [83, 84]