Extended Data Fig. 7. MYC directly regulates GCDH expression.
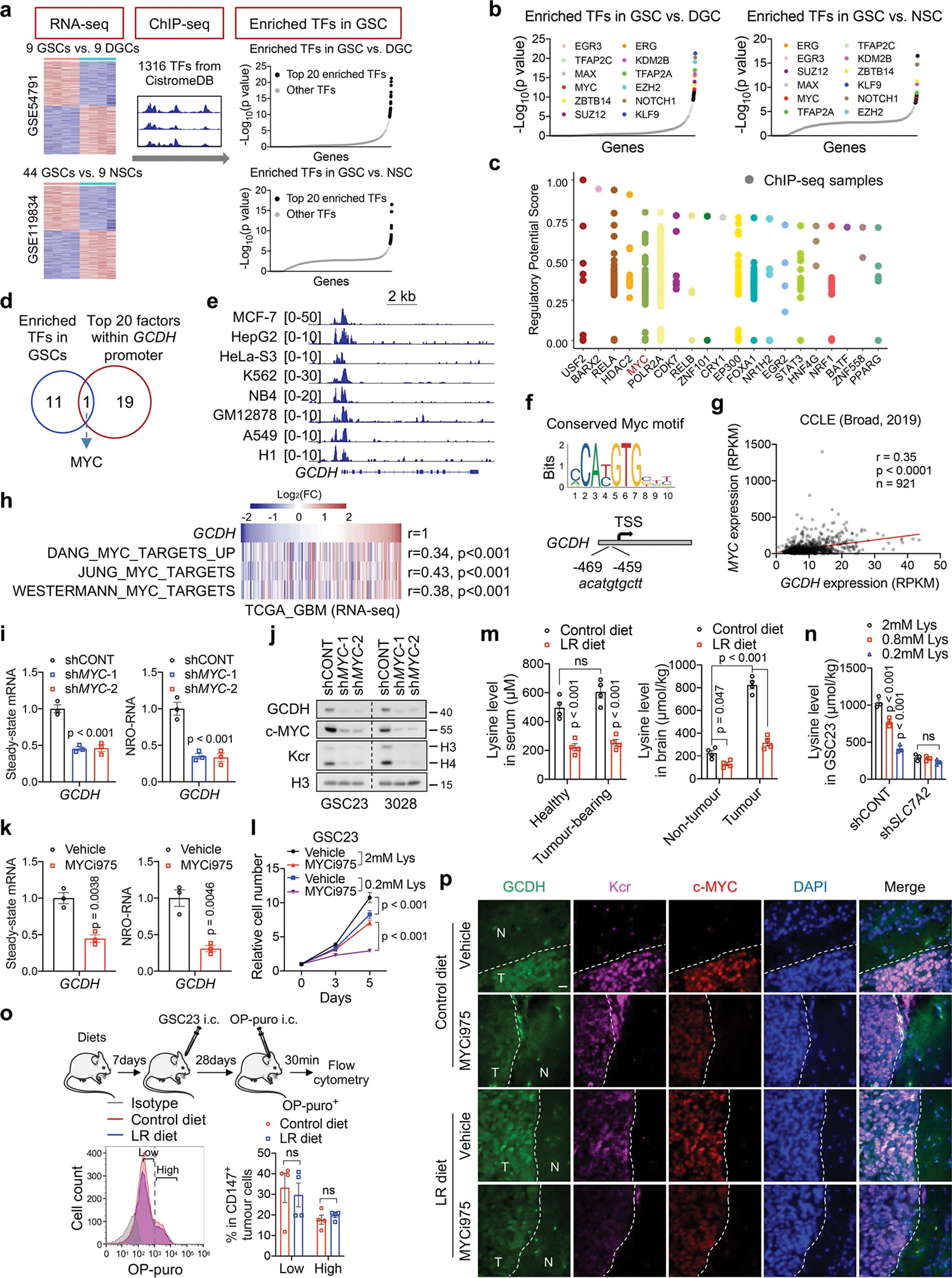
a, Diagram depicting the screening strategy to identify enriched TFs with selective dependency in GSCs.
b, 12 overlapped TFs responsible for DEGs between GSCs and DGCs/NSCs among the top 20 enriched TFs.
c, Top 20 upstream regulators for GCDH transcription, ranked by regulatory potential (RP) score from BETA algorithm. Each dot represents a ChIP-seq sample with analysed TFs labelled on the X axis. TFs with high RP scores are more likely to regulate GCDH.
d, Venn diagram showing the overlapped TFs.
e, MYC ChIP-seq tracks at GCDH gene locus in 8 human cell lines from ENCODE database.
f, The promoter of GCDH harbours a conserved MYC-binding element.
g, h, Correlation between GCDH and MYC mRNA (g) or signature (h).
i-k, RT-qPCR (i, k) and IB (j) analysis of steady-state mRNA, nascent transcripts or protein of GCDH in GSCs with or without MYC inhibition. NRO, nuclear run-on.
l, Cell proliferation of GSC23 cultured in indicated media and treated with or without 0.2 μM MYCi975 for 5 days.
m, Lysine levels in serum and brain tissues from healthy NSG mice or NSG mice bearing GSC23-derived intracranial tumours after dietary lysine restriction for 4 weeks (n = 4 biologically independent mice).
n, Intracellular lysine levels of GSC23 cultured in indicated media for 5 days.
o, Flow cytometry plots and quantification (n = 4 biologically independent mice) of protein synthesis rate in CD147+ human tumour cells as indicated.
p, IF staining of indicated sections from GSC23-derived intracranial tumours (n = 3 biologically independent mice). N, non-tumour; T, tumour. Scale bar, 20 μm.
Data are presented from three independent experiments in i, k, l and n. Representative of two independent experiments in j. Data are presented as mean ± SEM in i and k-o. Pearson’s correlation with two-tailed test for g and h, one-way ANOVA followed by multiple comparisons with adjusted p values for i, m and n, two-tailed unpaired t test for k and o, two-way ANOVA followed by multiple comparisons with adjusted p values for l. ns, not significant.
