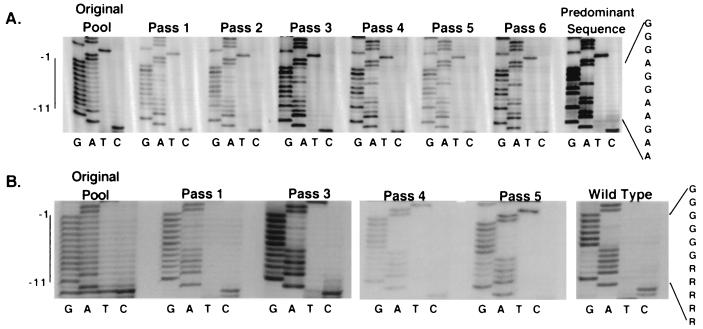
FIG. 3.
Evolution of randomized purine PPT pools. (A) Evolution of 179-member pool. Direct sequencing of uncloned PCR products containing the PPT region amplified from pools of unintegrated viral DNAs harvested from Rat2 cells infected with pool virus or of plasmid PCR products. At the left is the sequence of a PCR product of the original purine PPT plasmid pool, with the position of the core PPT indicated. Sequences of six successive passages of the pool are then shown. The sequencing reaction on the right is of a PCR product from a plasmid clone containing the predominant sequence that emerged after serial passage. At the far right is the predominant sequence. (B) Evolution of ∼6,300-member purine PPT pool. The original plasmid pool is on the left. Sequences of PCR products from viral DNA after passages 1, 3, 4, and 5 are shown, followed by the sequence of a wild-type PCR product. The predominant sequence is shown at the right.