Fig. 4 |. Pan-neuronal augmentation of Spargel rescues circadian rhythmicity in dfmr1 mutant flies.
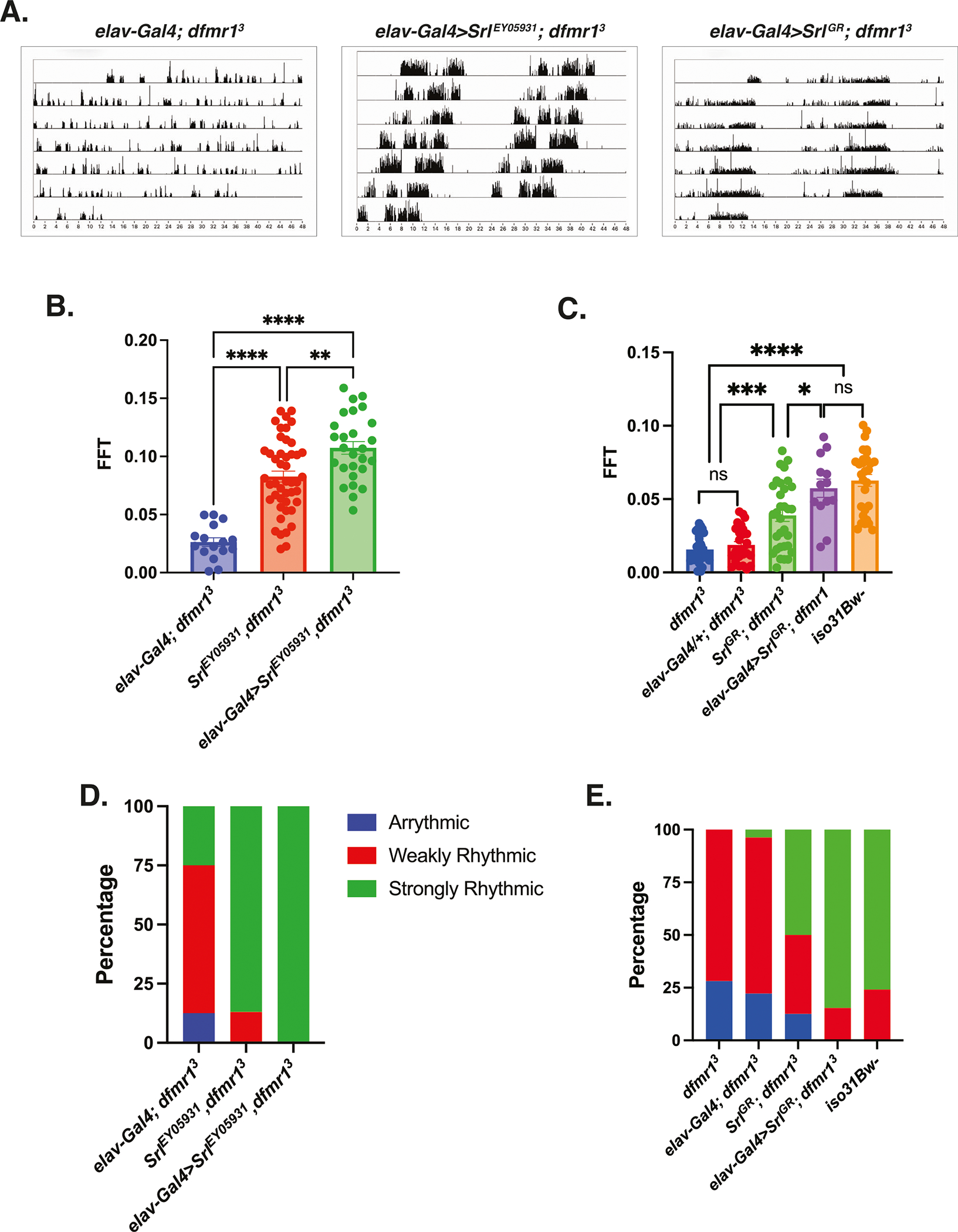
A–E Circadian behavior was evaluated by comparison of actogram appearance, the average fast Fourier transform (FFT) values, and percentage of rhythmic flies to ascertain whether augmentation of Spargel expression improves circadian behavior in dfmr1 mutant flies. Sample number (N) per genotype: (elav-Gal4; dfmr1) = 16–27; (SrlEY05931,dfmr1) = 46, (elav-Gal4>SrlEY05931,dfmr1) = 27, dfmr1 = 32, (SrlGR; dfmr1) = 32, (elav-Gal4>SrlGR; dfmr1) = 13, iso31Bw- = 29. A Representative actograms from flies of the genotypes indicated. In contrast to the free-running rest:activity rhythms of dfmr1 mutants that contain the elav-Gal4 transgene alone, dfmr1 mutants that contain the SrlEY05931 or SrlGR transcript in conjunction with the elav-Gal4 driver display consolidated, rhythmic behavior. B, C The average fast Fourier transform (FFT) was calculated for genetic combinations. One-way ANOVAs revealed a significant group effect for FFT values (p < 0.0001). Post hoc Tukey tests indicated that dfmr1 mutant flies that expressed the (B) SrlEY05931 or (C) SrlGR construct in conjunction with the elav-Gal4 driver had significantly higher FFT values compared to dfmr1 mutant flies that contained either transgene alone. Values represent mean ± SEM. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001. D, E The percentages of strongly rhythmic (FFT ≥ 0.04), weakly rhythmic (0.04 > FFT ≥ 0.01), and arrhythmic (FFT < 0.01) flies of each genotype are shown in green, red, and blue, respectively. The percentage of strongly rhythmic flies is increased in dfmr1 mutants that contained the (D) SrlEY05931 or (E) SrlGR construct in conjunction with the elav-Gal4 driver compared to either construct alone.
