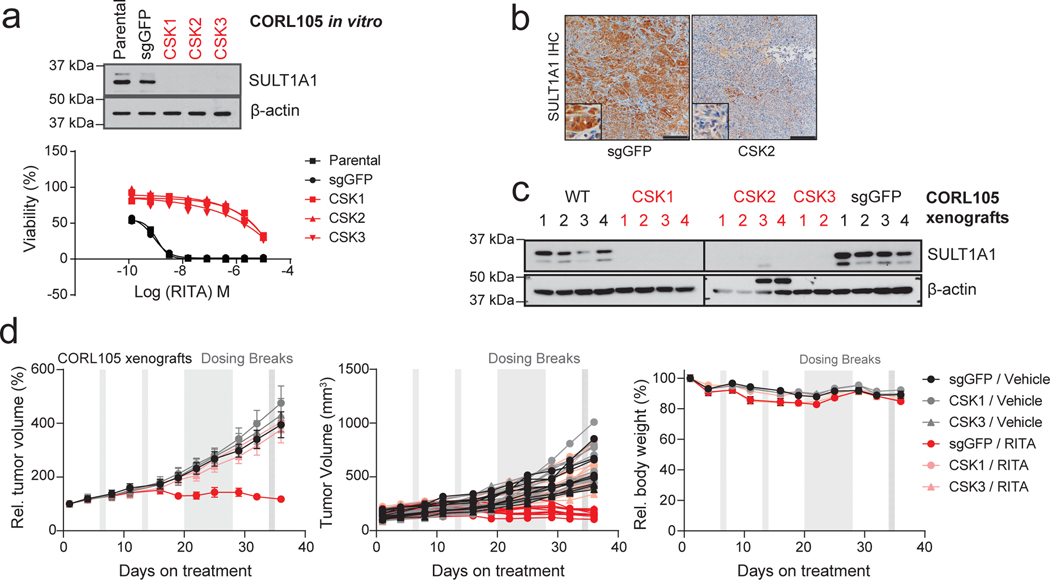
Extended Data Figure 9. SULT1A1 determines RITA efficacy in vivo.
a-d, Study of SULT1A1-dependent sensitivity of CORL105 xenograft model to RITA. CORL105 is an IDH1-R132C mutant lung adenocarcinoma cell line with high endogenous SULT1A1 levels, which has robust growth in vivo. a, Generation of CORL105 derivatives with CRISPR- mediated SULT1A1 KO. Upper, Immunoblot showing loss of SULT1A1 protein expression upon CRISPR-mediated deletion of SULT1A1 (CSK1–3) and robust SULT1A1 detection in parental CORL105 cells and control sgGFP cells. The immunoblot was performed two times with similar results. Lower, demonstration that CORL105 cells are highly sensitive to RITA in a SULT1A1- dependent manner. Two biologically independent experiments are shown. b, Representative immunohistochemistry staining from CORL105 control (sgGFP) and SULT1A1 KO (CSK2) xenografts, showing loss of staining with the SULT1A1 antibody in the SULT1A1 KO model.
Serves as validation of SULT1A1 antibody specificity for IHC studies. Similar results were obtained in samples from 2–4 independent animals per group and three groups with independent sgRNA designs targeting SULT1A1 gene. Scale bar, 200 μm. c, Immunoblot confirming SULT1A1 protein loss in xenograft tumors generated from SULT1A1 KO CORL105 cells. The immunoblot was performed a single time, with multiple independent tumors analyzed per condition. d, Mice harboring tumors of 100–150 mm3 were treated with RITA (100 mg/kg) or vehicle daily with intermitted dosing breaks. Graphs show serial monitoring of group tumor volume (left), individual tumor volume (middle) and body weight (right). Dosing breaks are denoted by grey shading. Error bars are mean ± SEM . n=5–10 independent animals per group.