FIGURE 2.
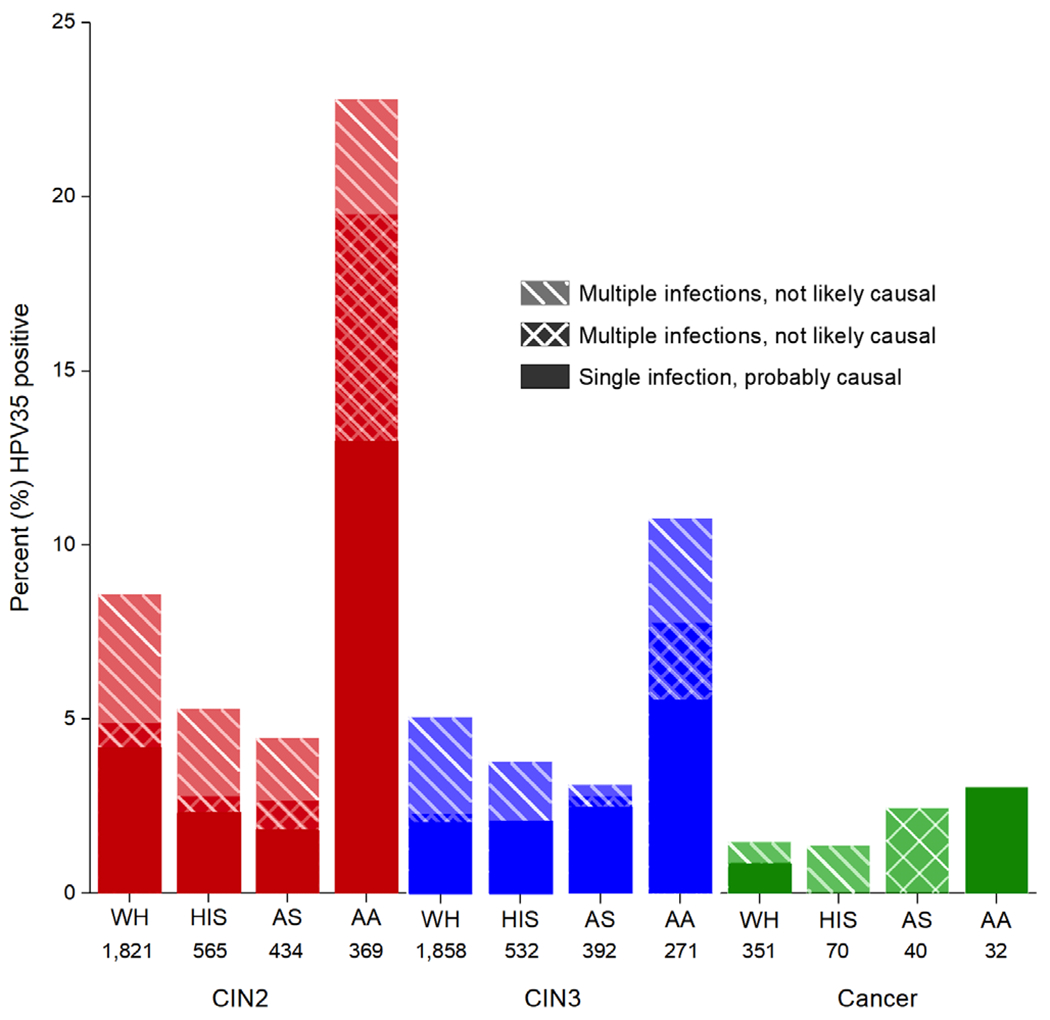
Prevalence of HPV35 among CIN2, CIN3 and cancer cases testing positive for carcinogenic HPV from 5 studies. CIN2, cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) grade 2; CIN3, CIN grade 3; WH, White; HIS, Hispanic; AS, Asian; AA, African-American. n, number of women with tested specimens. Among CIN2 and CIN3 cases, African-American women were more likely to have a “single HPV35 infection” (13.0% vs 3.5%, P < .001 for CIN2 and 5.5% vs 1.9%, P < .001 for CIN3) and both a “single HPV35 infection” and “HPV35 co-infection, most prevalent” (18.7% vs 4.2%, P < .001 for CIN2 and 7.4% vs 2.1%, P < .001 for CIN3). Differences were not statistically significant for cancers (P = .1). The number of cases from the studies presented in Table S5 and percent with 95% confidence intervals are presented in Table S2
