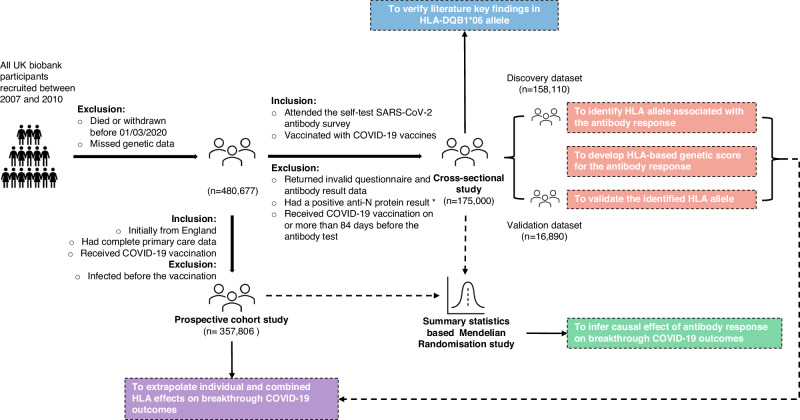
Fig. 1. Study design and flowchart.
Information about previous COVID-19 infection status was not available for all participants. Specifically, out of the 81,353 people who tested positive in the self-test antibody study, only 58,821 (72.3%) participated in the follow-up infection study and had a valid anti-N protein result. Of these, 10,783 (18.3%) tested positive for the anti-N protein and were excluded from the study. For the remaining 22,532 (27.6%) individuals who did not participate in the follow-up infection study, and thus had an undetermined prior infection status, we made an assumption that they were COVID-19 naïve and were included in the subsequent analyses. As a result, it is possible that about 5.0% (27.6% × 18.3%) of antibody-positive participants in the current cohort could result from the previous infection rather than the vaccination.