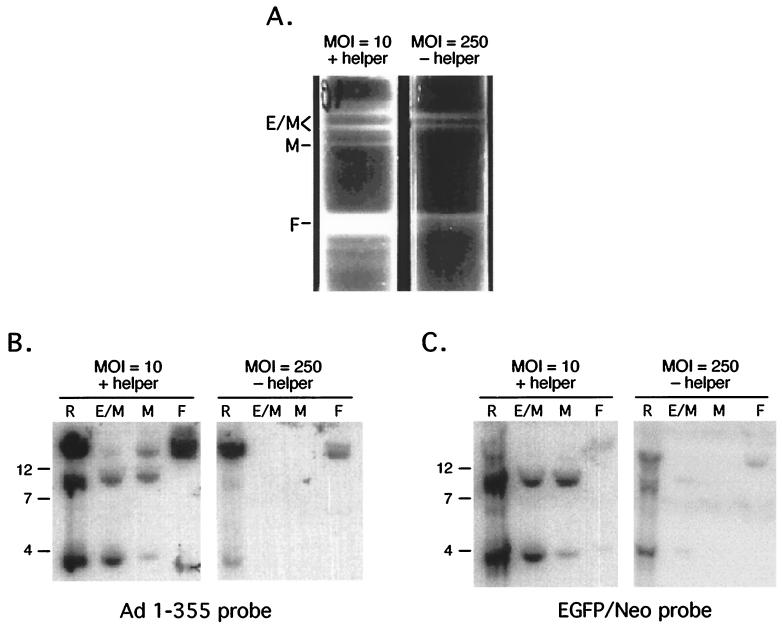
FIG. 5.
Molecular characterization of mAd. C12 cells were infected with CsCl2-purified Ad/AAV hybrid virus at an MOI of 10 PFU/cell, together with wild-type helper virus (MOI = 10 PFU/cell) or at an MOI of 250 PFU/cell without helper virus. (A) CsCl2 equilibrium ultracentrifugation of viruses produced in C12 cells. Recombinant mAds separated from the wild-type helper virus and the parental Ad/AAV hybrid viruses were separated by CsCl2 equilibrium ultracentrifugation. E/M, light virion mixture; M, middle fraction; F, full particles of Ad/AAV, heavy fraction. (B and C) Analysis of viral DNA from infected C12 cells. Replicated DNA was isolated 24 h after infection and analyzed by Southern blot (lanes R). Viral DNA was prepared from each fraction from the CsCl2 equilibrium gradient and analyzed by Southern blot (lanes E/M, M, and F). Membranes were hybridized either to Ad probe (1 to 355 bp) or to the EGFP/Neo cassette from the parent Ad/AAV. Markers are indicated in kilobase pairs on the left.