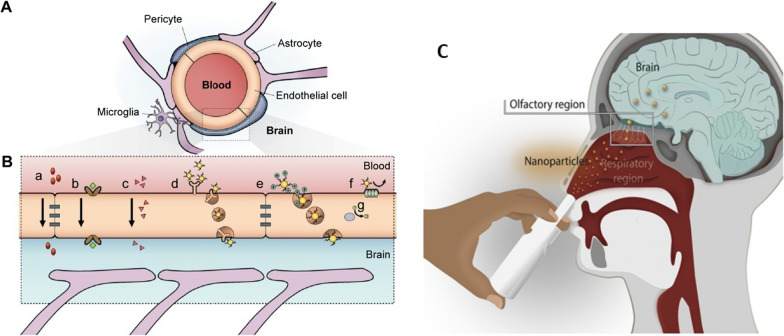
Fig. 3.
Principal pathways to overcome the BBB. A Scheme of the neurovascular unit of BBB constituted of pericytes, astrocytes, and endothelial cells. B The main mechanism of crossing through BBB: a) tight junctions restricting the pass of water-soluble compounds, b) carrier-mediated transport, [c] lipid-soluble agents, d) receptor-mediated endocytosis and transcytosis, e) adsorptive-mediated endocytosis and transcytosis, f) the efflux pump expulses the drugs from the endothelial cells to the blood, g) Cytochrome P450 enzymes. Adapted with permission from Ref. [126].
Copyright 2015, with permission from Dove Medical Press Limited. C Anatomical features of the intranasal route involved in nose-to-brain drug delivery. Adapted with permission from Ref. [133]. Copyright 2022, with permission from Elsevier