Figure 3. Affinity maturation of HCDR3-edited B-cell receptors.
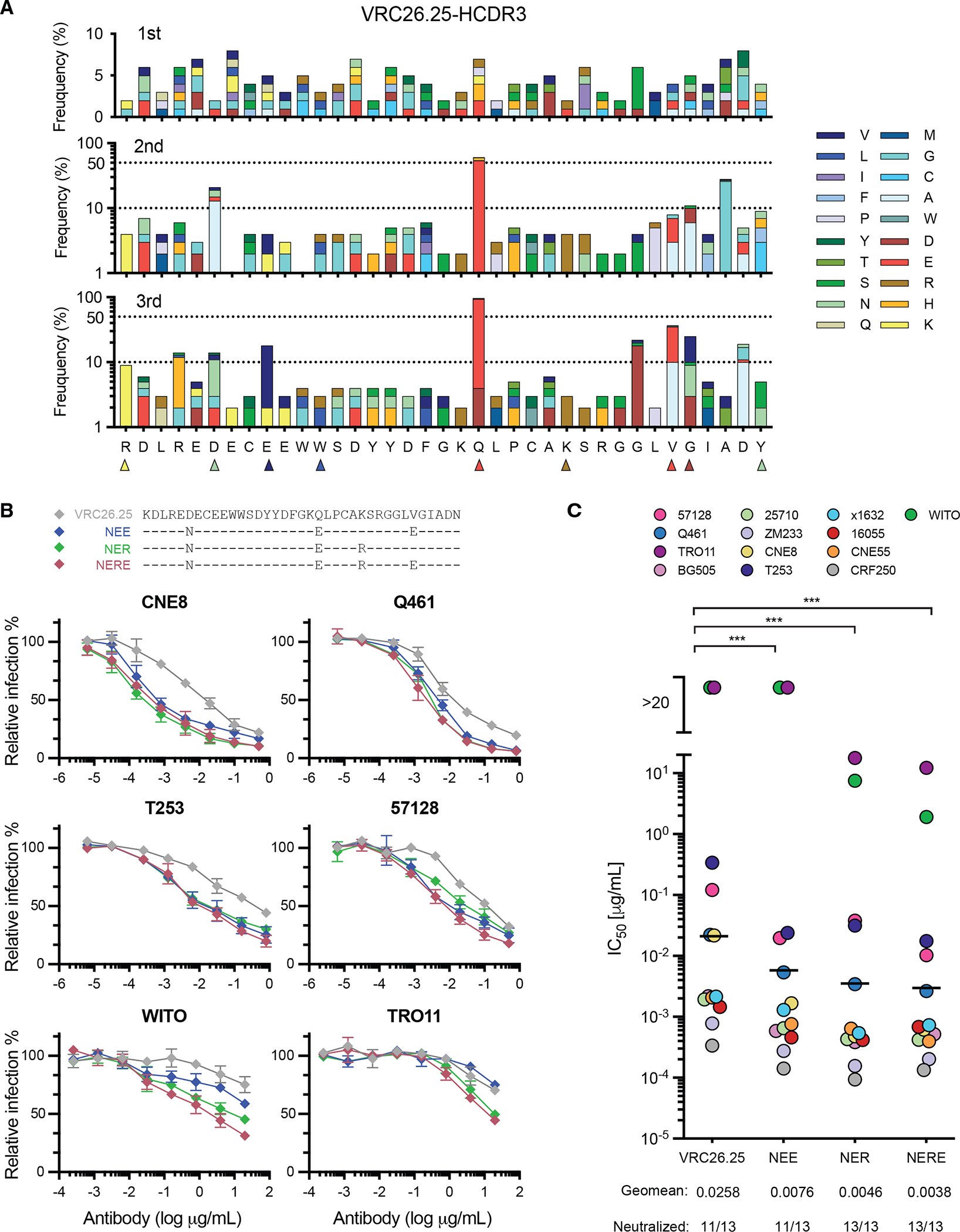
(A) The frequencies of amino acid mutations within the HCDR3 region present in edited clones were analyzed after the indicated immunization. The most frequent 9 mutations observed in more than one mouse group represented here, are marked with triangles, with colors indicating the mutated amino acid. These mutations are characterized in subsequent panels. Note that the first and last residues shown derive from murine VH1-family and JH4 segments, respectively, rather than the VRC26.25 HCDR3. (B) Top panel: Combinations of HCDR3 mutations identified in Fig. S2C as high affinity binders to ConM-SOSIP (v8.1ds) immunogens bearing either the CRF250 or BG505 V1V2 regions were introduced into full-length, unmodified VRC26.25. Bottom panels: These VRC26.25 variants were characterized for their ability to neutralize the indicated pseudoviruses, including two VRC26.25-resistant isolates (WITO and TRO11). (C) The same VRC26.25 variants were used to measure neutralization efficiency of the indicated global panel of HIV-1 isolates. IC50 values are represented in colored circles, with geometric mean values indicated by a line. Significant differences from wild-type VRC26.25 were determined by paired t-test (***p<0.001). Additional data is provided in Fig. S3.
