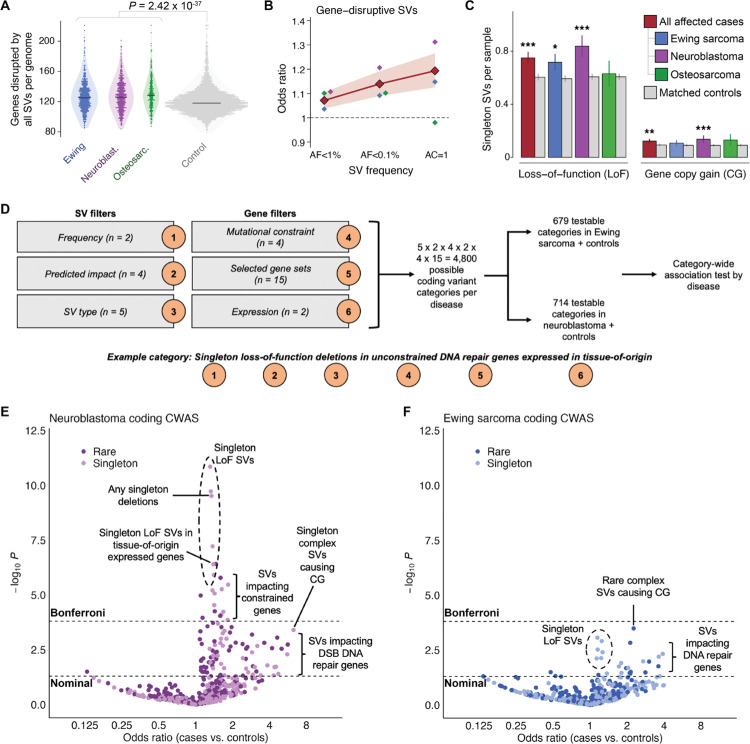
Fig. 3 |. Pediatric cancer patients carry an excess of rare germline SVs that impact disease-relevant genes.
(A) On average, the number of protein-coding genes disrupted by all germline SVs was significantly greater among pediatric cancer cases relative to adult controls. (B) Rare gene-disruptive SVs were enriched in cases versus controls, and this enrichment was inversely correlated with SV frequency. Shaded area indicates 95% CI for all histologies. (C) We found comparable enrichments in two independent subsets of singleton SVs with opposing predicted consequences on gene function: loss-of-function (LoF) and whole-gene copy gain (CG). (D) We carried out a category-wide association study (CWAS) in neuroblastoma and Ewing sarcoma, combining six layers of filters to categorize types of coding SVs for burden testing.37, 38 We evaluated 679 and 714 categories of gene-disruptive germline SVs in Ewing sarcoma and neuroblastoma, respectively. (E) In neuroblastoma, 27 categories of SVs exceeded Bonferroni significance, including singleton LoF SVs impacting mutationally constrained genes and genes expressed in adult adrenal gland. (F) In Ewing sarcoma, no single category of SVs was enriched in cases or controls at Bonferroni significance, although multiple categories of potential biological interest were nominally significant.