Figure 4.
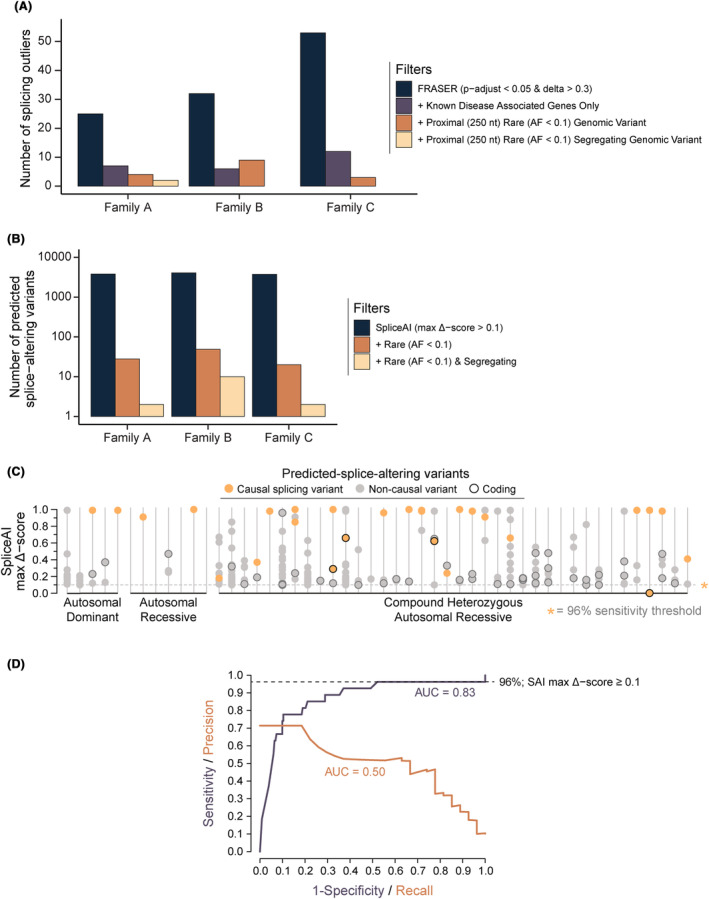
Trio genome sequencing data filters out highly scored but noncausal findings from in silico splicing analyses. (A) Deployment of FRASER to identify splicing outliers in 3 families with RNA‐Seq data available. Analyzing statistically significant splicing outliers identified by FRASER using the recommended thresholds (range 25–55 outliers per sample/case; adjusted p‐value <0.05 & effect‐size/delta‐psi ≥0.3) alongside genomic sequencing data was essential to reduce the large number of noncausal findings. In practice, by confirming the presence of a rare (allele frequency <0.1 and number of alternate allele homozygotes <5), segregating variant identified by genome sequencing proximal (±250 nt) to a splicing outlier all but two splicing outliers across the three families were excluded, substantially reducing the time required to manually validate candidate outliers (in Integrative Genomics Viewer 30 ). (B) Number of variants identified in genome sequencing data across all genes using SpliceAI delta score of ≥0.1 as threshold for a prediction of splice‐altering outcomes in the same three families as in S1a. Inclusion of trio segregation data reduced noncausal predicted‐splice‐altering variants by greater than 10‐fold. (C) Segregating rare variants from exome or genome data for 50 solved families with SpliceAI maximum delta scores ≥0.1. On average, families had 4.8 rare (allele frequency <0.1 & number of alternate allele homozygotes <5), noncausal predicted‐splice‐altering rare segregating variants in known NMD genes (n = 606). Searches were conducted in each family using the segregation of the known causal variant. For compound heterozygous recessive noncausal predicted‐splice‐altering variants, confirmation of a second rare variant in trans was not sought. Therefore, 4.8 noncausal predicted‐splice‐altering segregating variants per family is likely an overestimation. (D) Receiver‐operator characteristic curve showing a SpliceAI maximum delta score threshold of ≥0.1 results in a sensitivity of 96% for the detection of splice‐altering causal variants in the 50 solved families in S1c. Poor performance across the precision‐recall curve is indicative of the high number of noncausal segregating variants predicted to be splice‐altering by SpliceAI.
