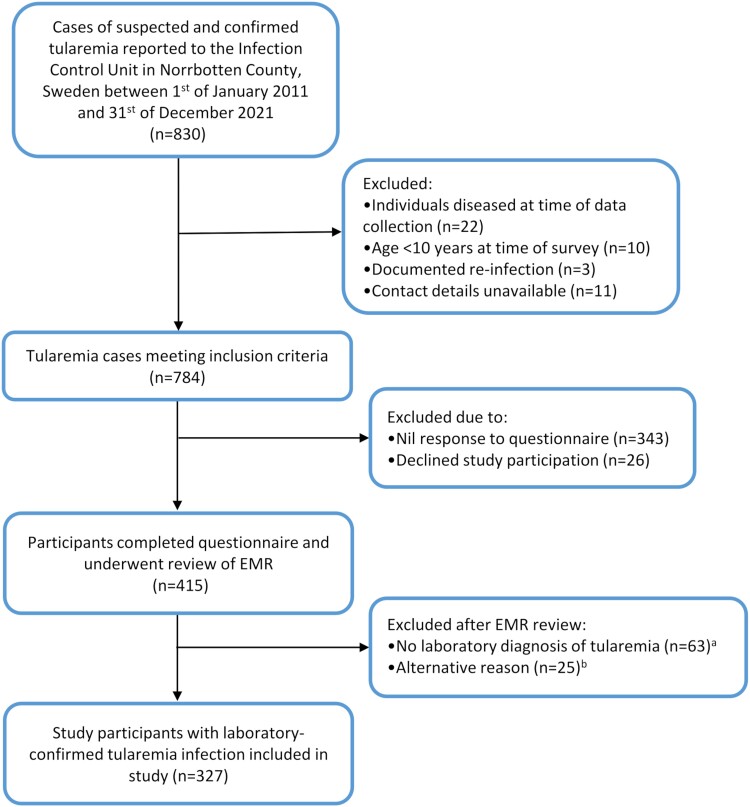
Figure 1.
Study method and inclusion of participants. EMR, electronical medical record. aLack of electronical medical record documentation (n = 15); confirmed false-positive tularemia tests (n = 2; ×1 false-positive rapid test, ×1 false-positive PCR); misdiagnosis (later confirmed as mycoplasma infection via PCR; n = 1); incidental positive serology without evident clinical symptoms of tularemia infection (n = 5); age <10 y at time of survey (n = 2). bClinical diagnosis of tularemia without a positive tularemia serology, culture, and/or PCR and were therefore excluded from further analysis (of these, 15 had a single negative serology result and 1 had a negative PCR result). PCR, polymerase chain reaction.