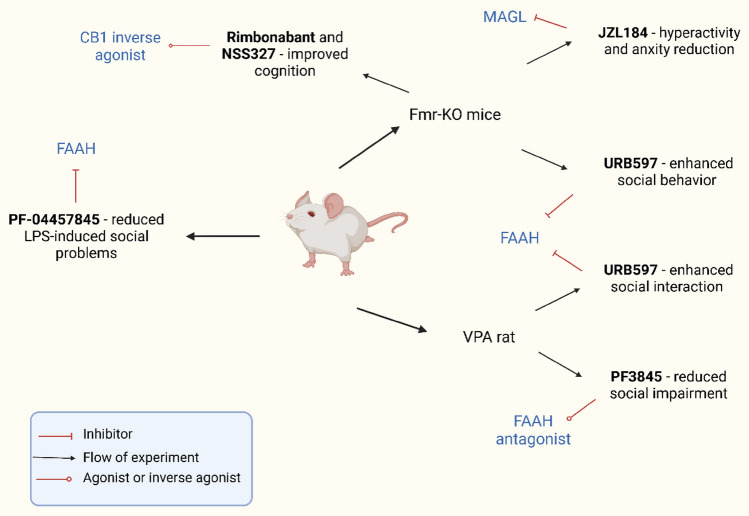
Fig. 1.
Simplified representation of the endocannabinoid (EC) system upon nerve stimulus. The endocannabinoids (AEA and 2-AG) trigger the CB1 receptors of presynaptic neurons. 2-AG is generated through hydrolysis of DAG by the DAGLα and DAGLβ enzymes, whereas AEA is synthesized through the action of NAPE-PLD enzyme. Membrane depolarization or nerve stimulation elevates the intracellular Ca2+ level that induces the 2-AG and AEA production in postsynaptic neurons. Retrograde attachment of AEA and 2-AG to CB1 receptors initiates downstream pathways that lowers Ca2+, reduces neurotransmitter release and leads to endocannabinoid degradation via MAGL and FAAH. Rimonabant and NESS3027 are two potential inhibitors of CB1 receptors. CB2 receptors are preferentially found in immune cells and reduce IL-1 expression. AM630 blocks CB2 receptors