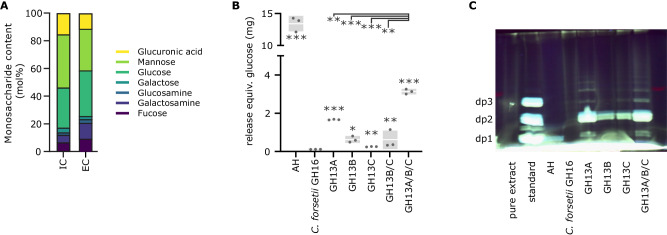
Fig. 5. Polysaccharide extracted from Polaribacter sp. Hel_I_88 contains high amounts of glucose in the form of α-glucan.
A Intracellular enriched extract (IC) or attached extracellular extract (EC) was subjected to acid hydrolysis (AH) and analyzed via HPAEC-PAD to determine monosaccharide composition (mol% of carbohydrate in the sample). IC was incubated with different recombinantly expressed Polaribacter sp. GH13s or Christiangramia forsetii GH16 laminarinase88 and analyzed via (B) reducing end assay (25 μg of protein incubated with 0.5% extract solution for 24 h) or (C) FACE. Pure polysaccharide extract and extract after acid hydrolysis (AH) were used as controls. For FACE analysis, a mixture of glucose (dp1), maltose (dp2) and maltotriose (dp3) was used as standard. Values of the reducing end assay are corrected against untreated extract. All (n = 3) non-0 values are shown (dots) alongside the standard deviation (gray bar) and mean value (white line). Significance (one-sided Student’s t test) is displayed as asterisks (significant to *0.05, **0.005, ***0.0005) either directly with the bar (to samples treated with C. forsetii GH16) or at the top (to a sample containing all tested Polaribacter sp. GH13s).