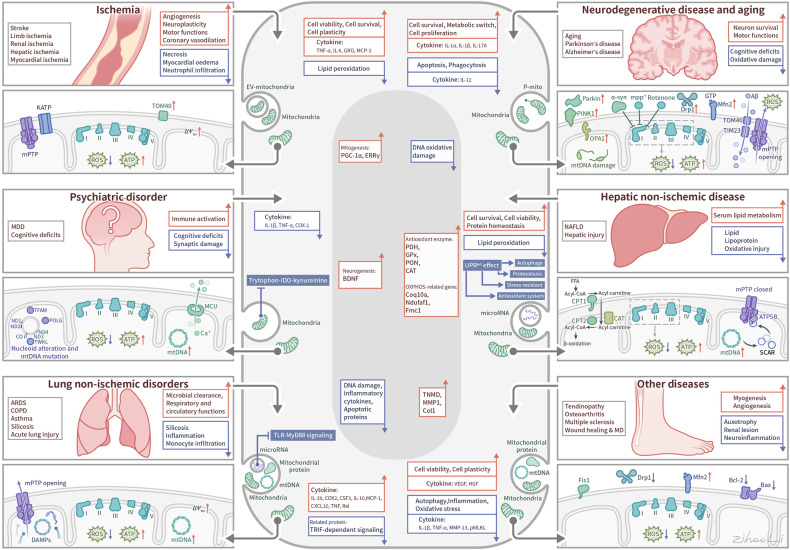
Fig. 5.
Therapeutic applications of mitochondrial and its component transplantation. This figure concludes therapeutic effects of mitochondria and associated components from different tissues and cells, to the mitochondria level (marked as grey arrows). The increased alterations in boxes are shown as up arrows while decreased alterations in boxes are shown as down arrows. Notably, though tissue level changes can vary, mitochondrial transplantation typically restores ATP production ability and reduces ROS production of damaged mitochondria. Besides, mitochondrial transplantation inhibited the intracellular try-IDO-kyn pathway, thereby improving the cognitive performance of psychiatric disorders and aging. In carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver injury, transplanted mitochondria can increase a series of anti-oxidative enzymes to improve OXPHOS functions by triggering the UPRmt pathway. On the other hand, MSCs also repress TLR-signaling of macrophages via microRNA transfers to reduce inflammatory responses