FIG. 3.
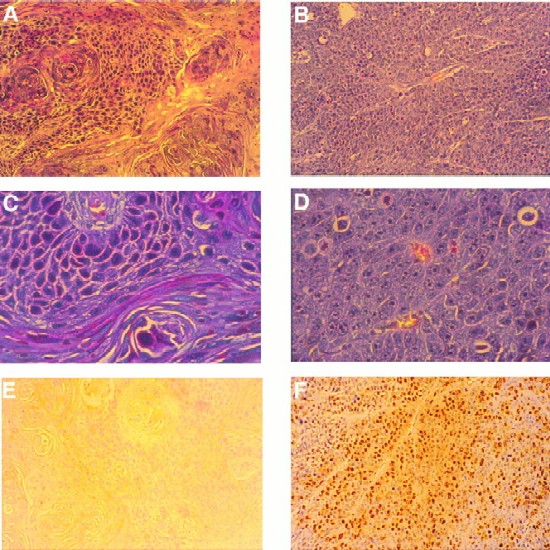
LMP2A expression induces tumorigenicity in nude mice. Hematoxylin-eosin stains of tumor sections of a parental tumor (A and C) and an LMP2A-induced tumor (B and D) are shown. Parental or LMP2A-expressing HaCaT cells (5 × 106) were injected subcutaneously into nude mice. The parental tumor, which appeared >8 weeks postinjection, was well differentiated, with a distinction between polarized and squamous cells. Abundant keratin whorls were detected. LMP2A tumors, which appeared after 1 to 2 weeks, were poorly differentiated. The cells contained large pleomorphic nuclei with distinct nucleoli. Blood vessels were abundant. No signs of differentiation were detected. (E and F) LMP2A-induced tumors were highly proliferative. Prior to sacrifice, animals were injected three times with BrdU at 50 mg/kg of body weight at 20-min intervals. Proliferating cells in the parental tumor (E) and the LMP2A tumor (F) were detected with an anti-BrdU antibody. Approximately 20 to 30% of the cells in LMP2A tumors stained positive for BrdU. Magnifications, A, B, E, and F, ×20; C and D, ×80.
