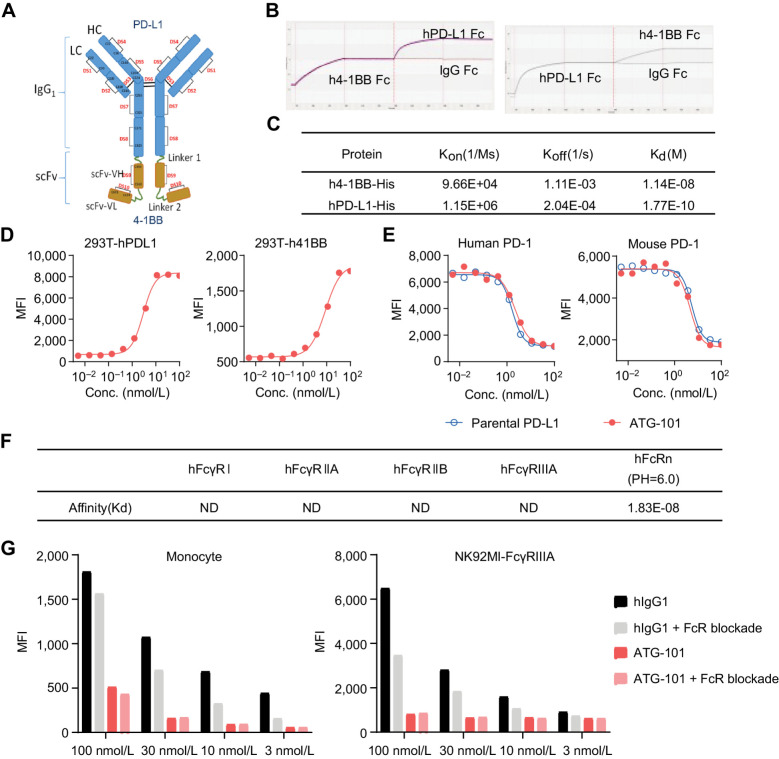
Figure 1.
ATG-101 binds to hPD‐L1 and h4-1BB simultaneously. A, Structure of ATG-101 BsAb. ATG-101 employs the IgG(H)-scFv structure, with the Fab arm targeting PD-L1 and the scFv targeting 4-1BB linked to the C-terminus of the FC domain. DS, disulphide bond. B, Binding capability of ATG-101 to hPD-L1/h4-1BB as determined by ForteBio. ATG-101 was immobilized on the biosensor, and the h4-1BB Fc (left) or hPD-L1 Fc (right) protein was injected first to bind ATG-101, whereafter hPD-L1 Fc (left) or h4-1BB Fc (right) protein was injected to bind. IgG-Fc was used as negative control. C, Kinetics parameter of binding affinity of ATG-101 to hPD-L1/h4-1BB. Kon, association rate constant; Koff, dissociation rate constant; Kd, dissociation constant, Kd = Koff/Kon. D, Binding of ATG-101 to 293T-hPDL1 (left) or 293T-h41BB (right). E, Blockade of the binding of biotinylated PD-1 protein to PD-L1 over expressed HEK293T cells by ATG-101 or parental PDL1 Ab. In D and E, n = 3, data representative of three independent experiments. F, Summary of binding affinity of ATG-101 to Fcγ receptor and FcRn as determined by ForteBio. ND, not detected. G, Binding of ATG-101 and human IgG1 control antibody to human monocytes and NK92MI-FcγRIIIA cells detected by flow cytometry. Representative of n = 3.