FIGURE 3.
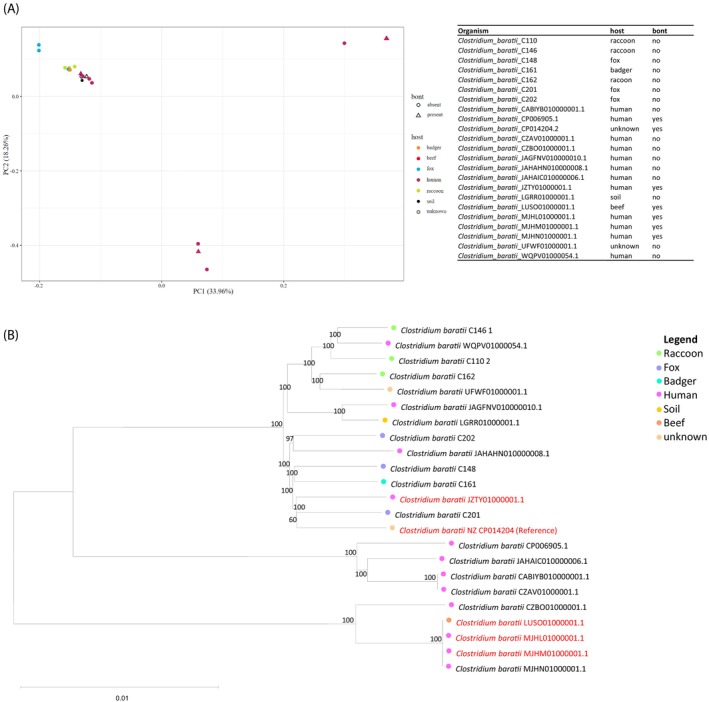
Pan‐genome‐based clustering of Clostridium baratii. (A) Pan‐genome‐based principal component analysis based on 23 C. baratii genomes. Seven genomes from this study and 16 genomes deposited at GenBank were used. Host and presence of the Botulinum Neurotoxin gene (bont) are indicated by colour code and shapes, respectively. (B) Neighbour‐joining phylogenetic tree based on core genome single nucleotide polymorphisms of 23 C. baratii genomes. Seven genomes from this study and 16 genomes deposited at GenBank were used. Genomes encoding botulinum neurotoxin are marked in red. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (100 replicates) is shown next to the branches. Evolutionary distances were computed using the Maximum Composite Likelihood method and are in the units of the number of base substitutions per site. The rate variation among sites was modelled with a gamma distribution (shape parameter = 0.5). All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated (complete deletion option). There were a total of 2,257,623 positions in the final dataset. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA11.
