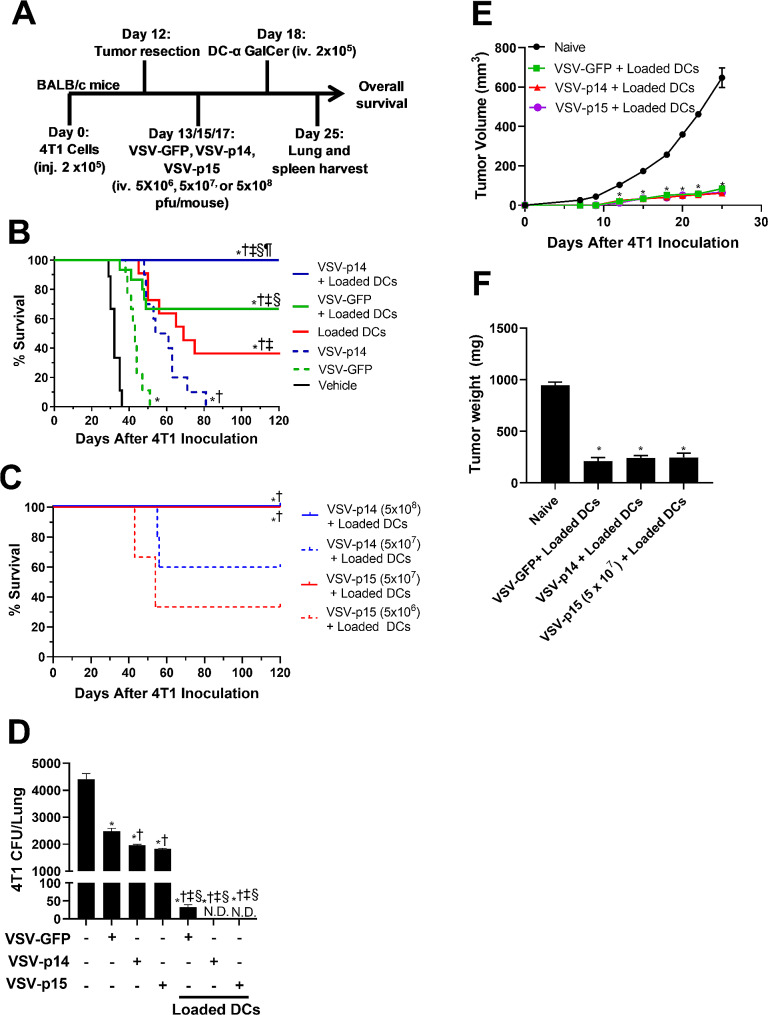
Fig. 5.
Combination therapy controls lung metastasis in a metastatic breast cancer model. (A) Schematic of the metastatic 4T1 tumor model and treatment schedule. (B) Overall survival was assessed in untreated tumor-bearing mice and mice treated with VSV-GFP or VSV-p14, alone and in combination with NKT cell immunotherapy mediated by transfer of α-GalCer-loaded DCs (n = 9–14 per group). *p < 0.05 compared to untreated, †p < 0.05 compared to VSV-GFP, ‡p < 0.05 compared to VSV-p14, §p < 0.05 compared to Loaded DCs. ¶p < 0.05 compared to VSV-GFP + glycolipid-loaded DCs. (C) Overall survival was assessed in mice receiving different doses of VSV-p14 or VSV-p15 in combination with NKT cell immunotherapy (n = 3–8 per group). *p < 0.05 compared to VSV-p15 (5 × 106) + glycolipid-loaded DCs, †p < 0.05 compared to VSV-p14 (5 × 107) + glycolipid-loaded DCs. (D) Lungs were isolated and dispersed into single cell suspensions to assess metastasis of 4T1 cells by colony-forming assay in the presence of 6-thioguanine (n = 4–7 per group). *p < 0.05 compared to untreated, †p < 0.05 compared to VSV-GFP, ‡p < 0.05 compared to VSV-p14, §p < 0.05 compared to VSV-p15. (E, F) Treated mice that survived to day 120 (Fig. 5B, C) were re-challenged in the contralateral mammary fat pad with 4T1 cells. Tumor (E) volume and (F) tumour weight were compared to naïve mice inoculated with 4T1 cells. *p < 0.05 compared to naïve control