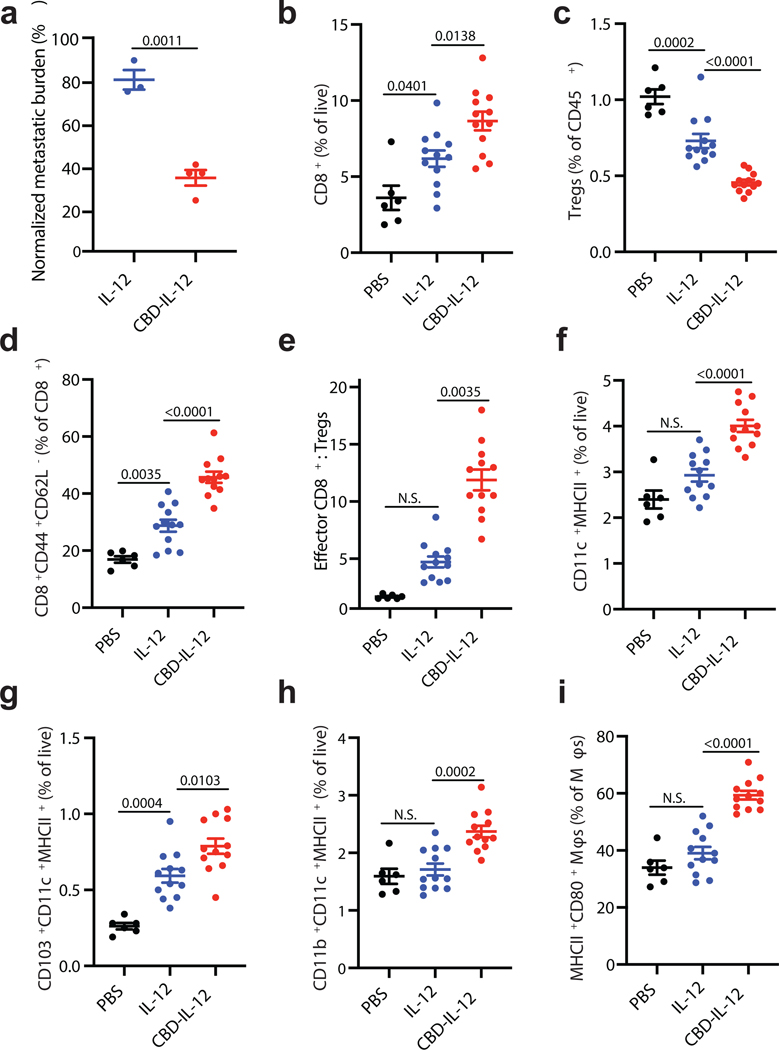
Fig. 5 |. CBD-IL-12 decreases metastatic tumour burden by triggering activation of innate and adaptive compartments of the immune system in the pulmonary metastatic model of B16F10 melanoma.
a, 5 × 105 B16F10 cells were injected i.v. on day 0. Mice were treated with either 25 μg IL-12 (n = 3) or with equimolar CBD-IL-12 (n = 4) i.v. once on day 8 and sacrificed on day 17. Metastatic burden was quantified using ImageJ software and normalized by total area of the lung. b-i, 2.5 × 105 B16F10 cells were injected i.v. on day 0. Mice were treated with either PBS (n = 6), 25 μg IL-12 (n = 12) or with equimolar CBD-IL-12 (n = 12) i.v. once on day 9 and lungs were collected on day 18. 2 × 106 live cells/well were plated for flow cytometric analysis. b, Percentages of CD3+CD8+ T cells within live cells. c, Frequency of CD3+CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs within lung-infiltrating immune cells (% of CD45+). d, Frequency of CD3+CD8+CD44+CD62L− effector CD8+ T cells within total CD8+ T cells. e, Ratio of effector CD8+ T cells to Tregs. f-h, Percentages of DCs (CD11c+MHCII+F4/80−) (f), CD103+ DCs (g), and CD11b+ DCs (h) within live cells. i, Frequency of MHCII+CD80+ macrophages within total macrophages (defined as CD11b+F4/80+). Lines represent mean ± SEM. Antitumor efficacy experiment (a) was performed twice, with similar results. Flow analysis was performed once on independent biological samples. Statistical analyses were done using unpaired, two-tailed t-test with Welch’s correction (a), ordinary one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test for parametric data (b,c,d,f,g,h,i) and Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison for nonparametric data (e).