Figure 2.
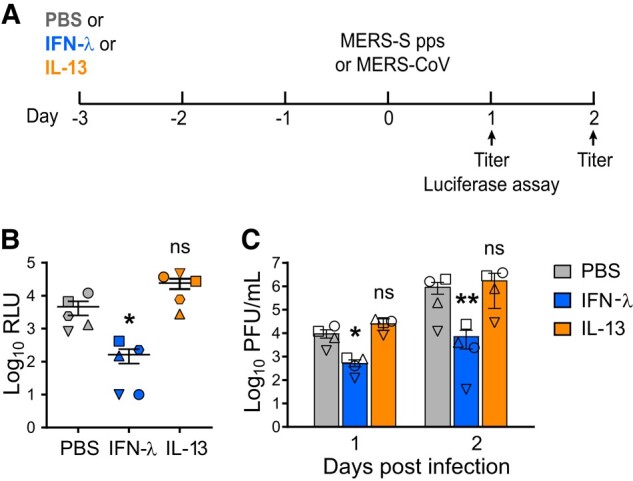
Short-term exposure to IL-13 has little effect on MERS-CoV entry and infection. A, Experimental design for testing MERS-CoV entry and replication in HAE. Briefly, HAE were maintained for 3 days in medium containing IFN-λ (1 ng/mL) or IL-13 (20 ng/mL) and then transduced apically with MERS-S pps or infected with MERS-CoV (MOI, 0.5). B, MERS-S pps entry was quantified by measuring luciferase activity in cell lysates at 24 hours posttransduction. Data points represent individual HAE donors, and data are plotted as mean ± SE (n = 5). Log-transformed data were tested for significant differences by repeated measures 1-way ANOVA, followed by a Tukey multiple-comparison test. C, Following apical infection with MERS-CoV, a plaque assay was used to measure apically released viral progeny at 1 and 2 days postinfection. Data represent mean ± SE (n = 4). Log-transformed data were tested for statistically significant differences relative to the PBS control at the indicated time points by repeated measures 2-way ANOVA, followed by a Sidak multiple-comparison test. *P < .05. **P < .01. ANOVA, analysis of variance; HAE, human airway epithelia; IFN-λ, interferon λ; IL-13, interleukin 13; MERS-CoV, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus; MERS-S pps, MERS S protein pseudoparticles; MOI, multiplicity of infection; ns, not significant; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; PFU, plaque-forming units; RLU, relative light units.
