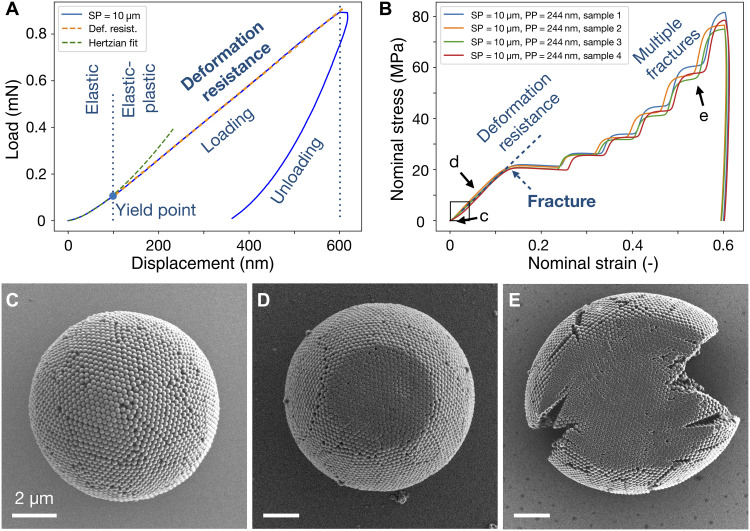
Fig. 2. Mechanical properties of PS colloidal SPs under compression in 50% ambient humidity.
(A) Load-displacement curve of a typical colloidal SP consisting of 244-nm primary PS particles during loading and unloading. After initial elastic deformation, the SP undergoes a linear region of elastic-plastic deformation, the slope of which represents the resistance against deformation under compression. The area under loading and unloading curve indicates toughness and the stored elastic energy during deformation. (B) Nominal stress-strain curves for four individual SPs, highlighting the reproducible compression behavior. (C to E) SEM images at different stages of the compression experiment. The SP (C) first deforms elastic-plastically at the beginning of compression (D) and then undergoes multiple fracturing indicated by pop-ins (plateaus) as the material fails (E). The SP is ductile, and individual PPs are heavily deformed.