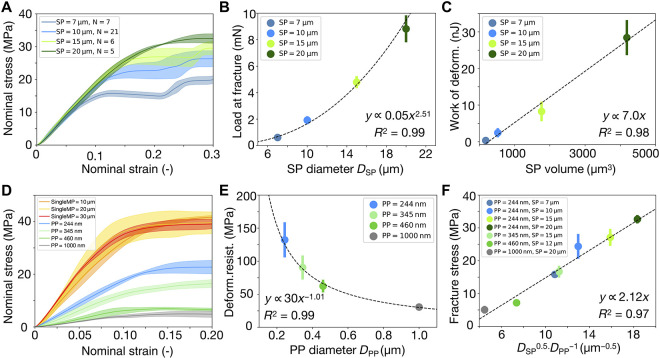
Fig. 3. Influence of SP and PP diameter on the mechanical response of SPs under compression.
(A) The deformation resistance, which can be considered the equivalent of a Young’s modulus in the SPs, is independent of SP diameter (PP diameter = 244 nm), indicated by the linear region of nominal stress-strain curves. (B) The fracture load of SP scales with its diameter via a power law with an exponent of 2.5. (C) The work of deformation is linearly proportional to the volume of SPs. (D) The deformation resistance of SPs increases as the PP diameter decreases (gray to green to blue), approaching the value of single large PS particles (yellow, pink, and red). (E) The deformation resistance of SPs scales inversely with the PP diameter. (F) Universal scaling relationship between fracture stress and the diameters of SPs and PPs. SDs are shown as error bars. In some cases, the error is smaller than the data points.