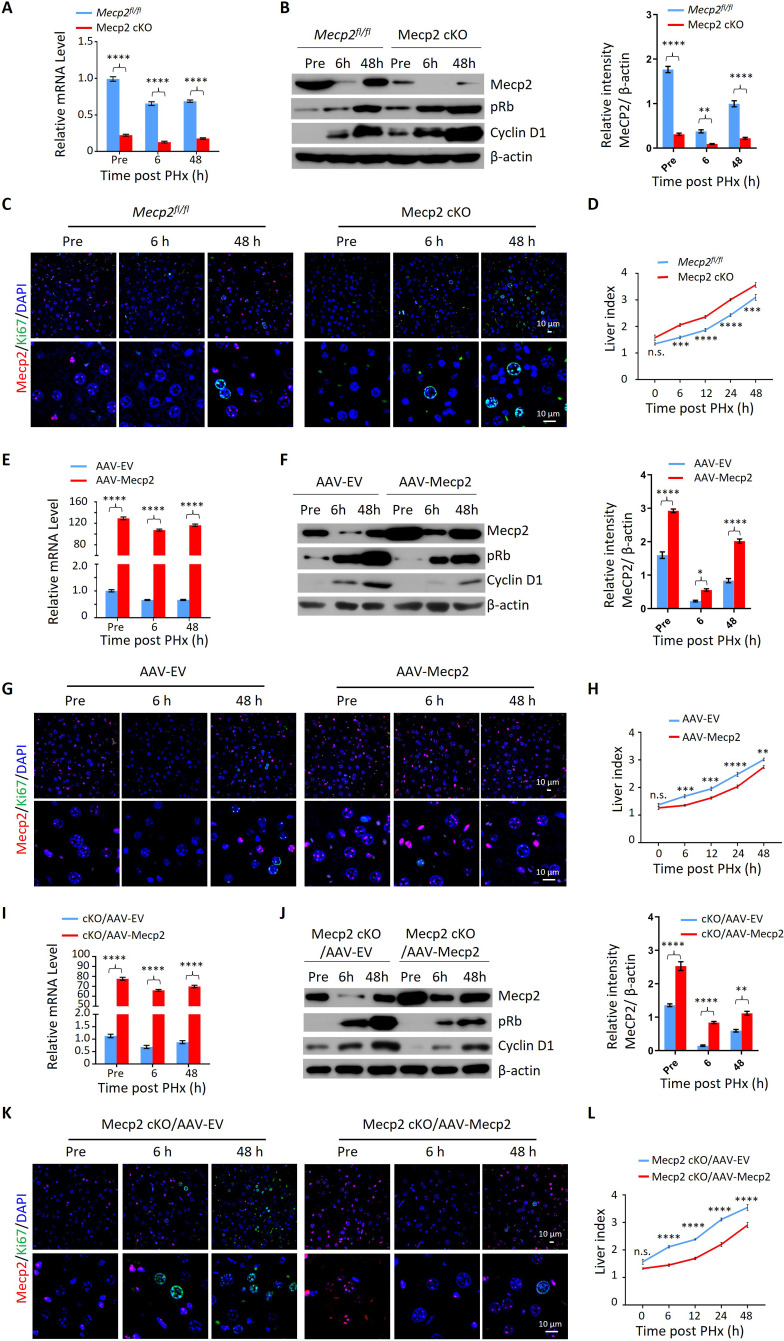
Figure 2. Mecp2 fine-tunes quiescence exit in hepatocytes after partial hepatectomy (PHx) in vivo.
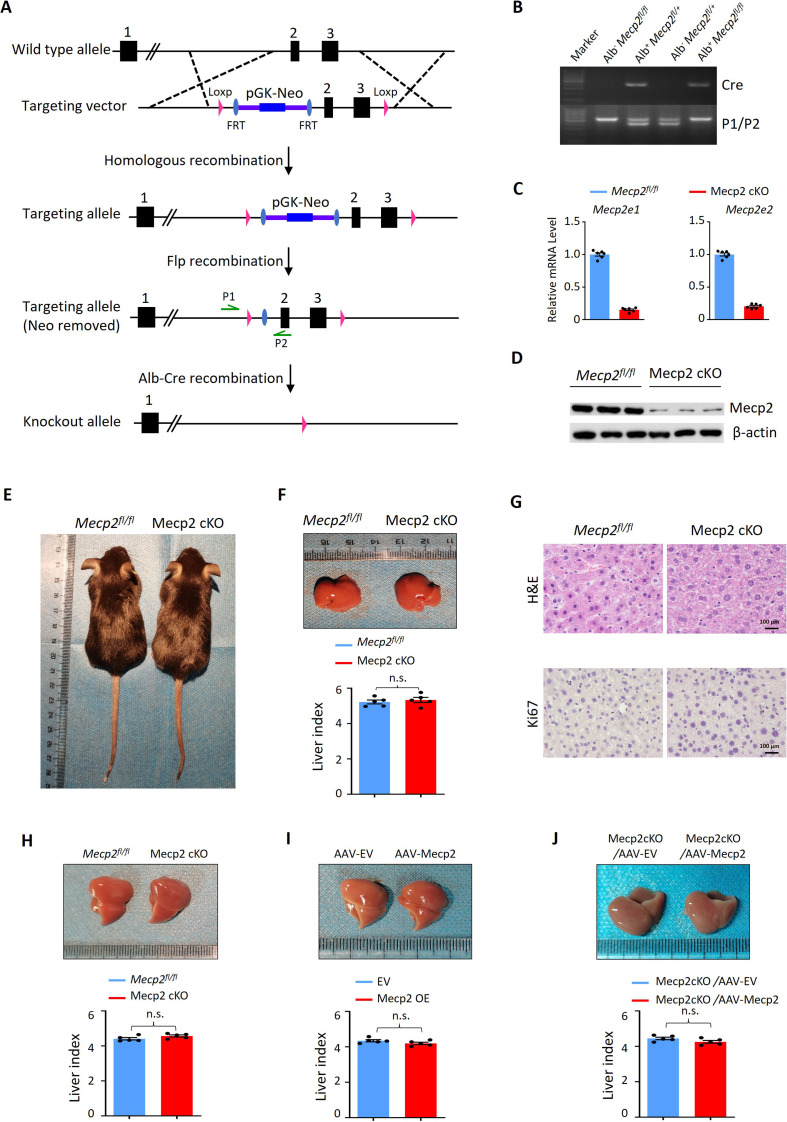
(A–D) Liver regeneration in Mecpfl/fl and Mecp2 cKO mice after PHx. (A) Real-time PCR to measure mRNA levels of Mecp2. The effects and corresponding quantification of Mecp2 KO on quiescence exit and liver regeneration were assessed by western blotting (WB) of Mecp2, pRb, and Cyclin D1 (B), immunofluorescence (IF) staining of Mecp2 (red) and Ki67 (green) in liver sections (C), and liver index of control and Mecp2 cKO mice (D) at the indicated time points. (E–H) Liver regeneration in Mecp2fl/fl livers without (AAV-EV) or with AAV-mediated Mecp2 OE (AAV-Mecp2) after PHx. AAV, adeno-associated virus; EV, empty vector. (E) Real-time PCR to measure mRNA levels of Mecp2. (F–H) The effects and corresponding quantification of Mecp2 OE on quiescence exit and liver regeneration were assessed by WB of Mecp2, pRb, and Cyclin D1 (F), IF staining of Mecp2 (red) and Ki67 (green) in liver sections (G), and liver index at the indicated time points (H). (I–L) Liver regeneration in Mecp2 cKO livers without (Mecp2 cKO/AAV-EV) or with AAV-mediated Mecp2 restoration (Mecp2 cKO/AAV-Mecp2) after PHx. (I) Real-time PCR to measure mRNA levels of Mecp2. (J–L) The effects and corresponding quantification of Mecp2 restoration on quiescence exit and liver regeneration in Mecp2 cKO livers were assessed by WB of Mecp2, pRb and Cyclin D1 (J), IF staining of Mecp2 (red) and Ki67 (green) in liver sections (K), and liver index (L) at the indicated time points. Data are presented as means ± SEM. In (A, E, I), n = 6; (B, F, J), n = 3; in (D, H, L), n = 5 mice/group. n.s., not significant; *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001 by two-way ANOVA.