Figure 3. Stem nanoparticles selectively expand VH1–18 QxxV bnAb precursors from physiological frequency in the antibody repertoire and induce diversification through somatic hypermutation in GCs.
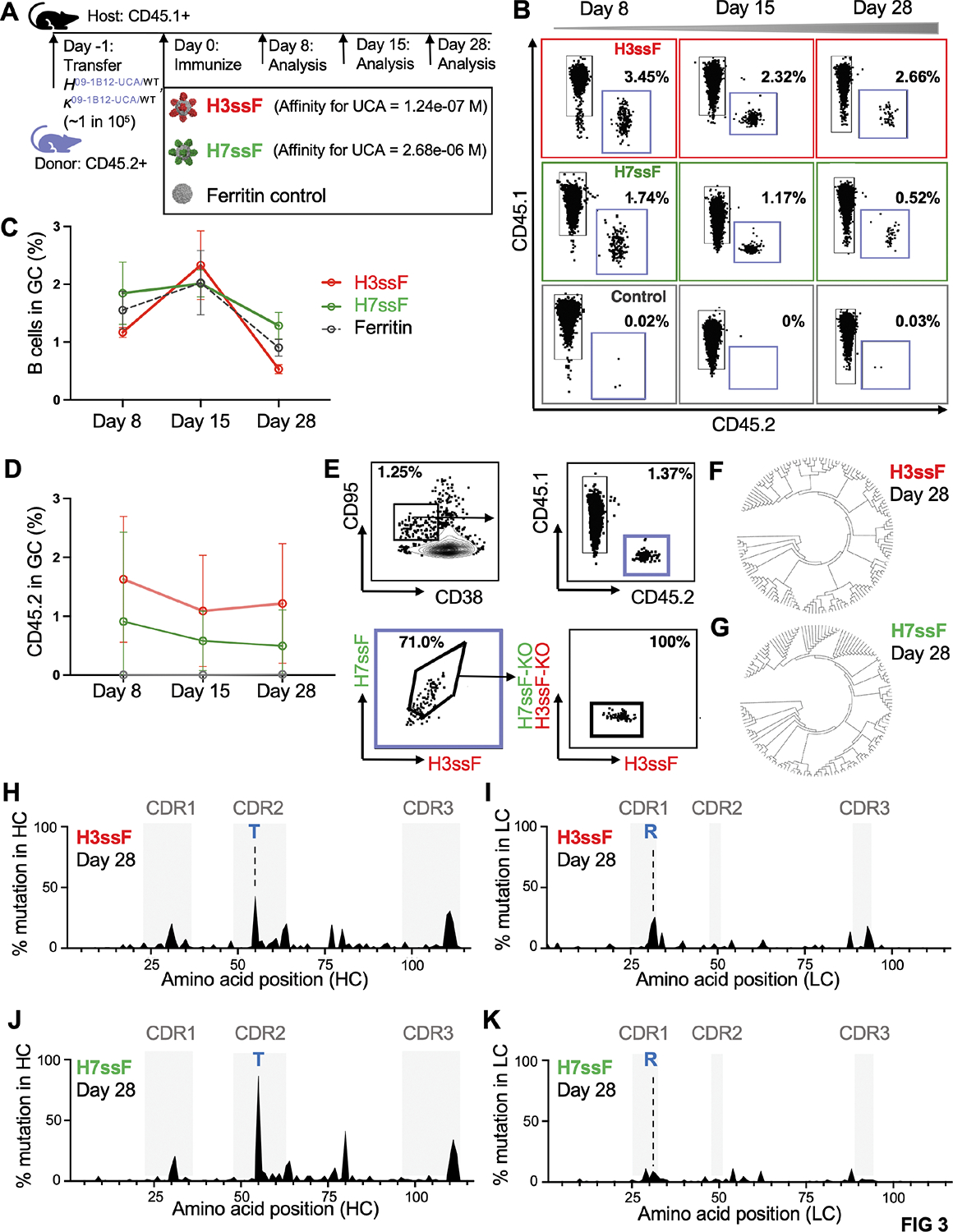
(A) Schematic of adoptive transfer performed at precursor frequencies of ~1 per 105 09–1B12-UCA B cells into WT mice at day −1 and subsequent single immunization of higher affinity H3ssF or lower affinity H7ssF. Naked ferritin particles were also given as a control. All vaccines were adjuvanted by the Sigma Adjuvant System. Spleens were sampled at the time points indicated. (B) Representative flow plots of CD45.2 B cells being recruited to GCs at days 8, 15, and 28 post-vaccination. (C) The percentage of GC B cells in the CD45.1 host was quantified at each time point (n=5 mice per immunogen, mean ± SD, one experiment). (D) The percentage of CD45.2 B cells within the host GCs each time point (n=5 mice per immunogen, mean ± SD, one experiment). (E) The GC CD45.2 B cells were also marked by epitope specificity to the central stem site [H3ssF+/H7ssF+/H3ssF-KO−/H7ssF-KO− (central stem epitope KO =N-linked glycan at 45HA2)] and single GC CD45.2 B cells in this gate were sorted by FACS and subjected to BCR sequencing. Results presented in B-E were recapitulated if H7 and H3 trimers were used (instead of nanoparticles) as the antigen B cell probes (Figure S5C–G). (F, G) HC nucleotide diversification of H3ssF+/H7ssF+/H3ssF-KO−/H7ssF-KO− B cell clones at 28 days after immunization with H3ssF or H7ssF. (H) Mutation frequency in the HC amino acid sequence at 28 days post immunization with H3ssF. (I) Mutation frequency in the paired LC amino sequence at 28 days post immunization with H3ssF. (J) Mutation frequency in the HC amino sequence at 28 days post immunization with H7ssF. (K) Mutation frequency in the paired LC amino sequence at 28 days post immunization with H7ssF. (H-K) Blue letters mark enrichment of amino acid mutations also present in mature 09–1B12 and 16.g.07. Data from (F-K) is from 125 GC BCRs for H3ssF (n=3 mice), 111 GC BCRs for H7ssF (n=3 mice); one experiment. See also Figure S5 (in relation to A–E) and Table S4 (in relation to F–K).
