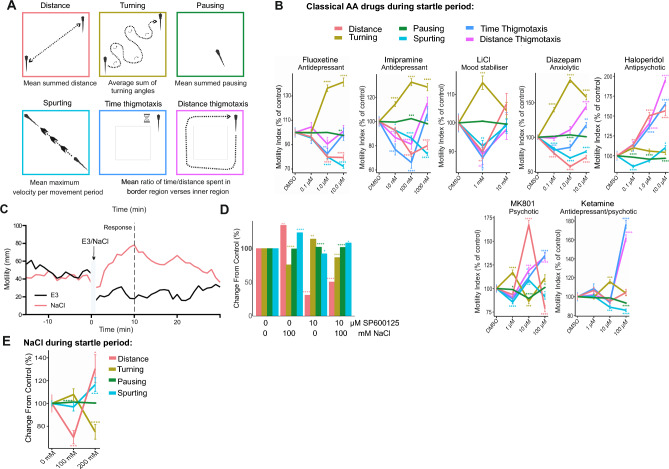
Figure 2.
Testing the effect of AA drugs on zebrafish larvae behavioural sequalae during the 1 min startle phase. (A) The behavioural features extracted from zebrafish larvae tracking are shown. Distance, turning, pausing, spurting, time and distance thigmotaxis are extracted using R statistical computing platform. (B) Fish were exposed to AA drugs and ketamine, MK801 or haloperidol as indicated and features (distance, turning, pausing, spurting, time and distance thigmotaxis) were extracted from the entire 1 min startle period. Averaged data indicates change relative to control for each of these behaviours according to colour code. (C) Mean motility profiles of zebrafish larvae (5 dpf) before and after E3 (n = 24) or NaCl (100 mM, n = 24) are shown. (D) Mean distance travelled, turning, pausing, and spurting of zebrafish larvae (5 dpf) before and during the 10 min after 100 mM NaCl (n = 72) or control (n = 67), are plotted as a % change from control. (E) Zebrafish treated with E3 medium or NaCl as indicated underwent the battery test. Mean data on distance travelled, turning, pausing and spurting are shown. Control: 15 (75 observations), NaCl: 32 (156 observations). P-values were calculated by Wilcoxon Rank Sum test and adjusted with Benjamini–Hochberg procedure, where * p-value ≤ 0.05; ** p-value * ≤ 0.01; ***p-value ≤ 0.001; ****p-value ≤ 0.0001.