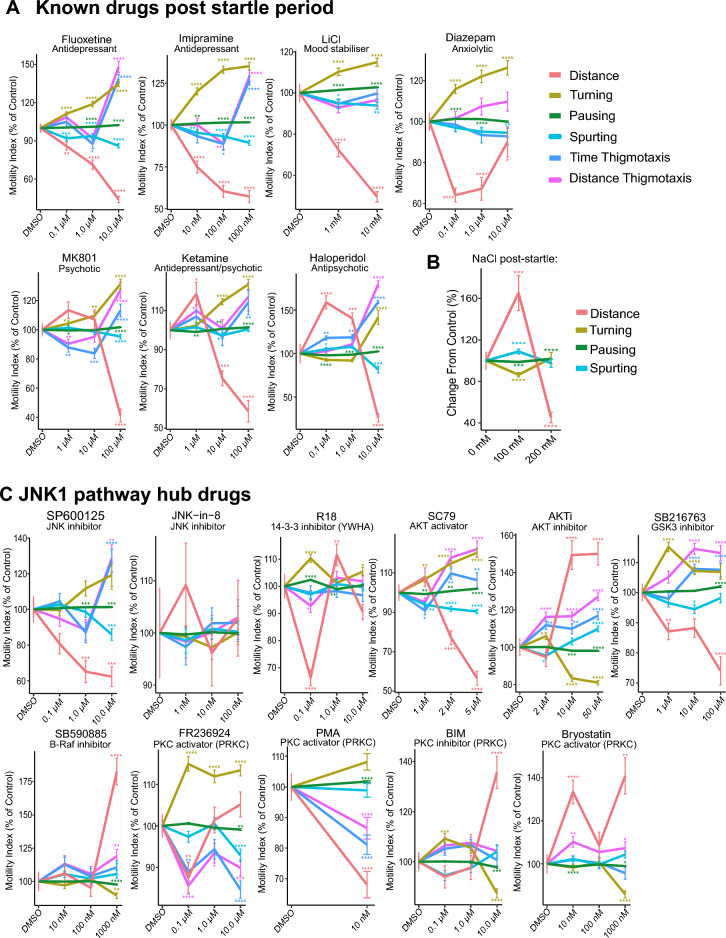
Figure 5.
Testing the effect of AA drugs and JNK1 pathway hub drugs on zebrafish larvae behaviour during the post-startle period. (A) Fish were exposed to AA drugs and ketamine or MK801 doses as indicated and new features (distance, turning, pausing, spurting, time and distance thigmotaxis) were extracted from the first 10 min following the 1 min startle period. Averaged data from the following fish measurement numbers: diazepam: 337, fluoxetine: 338, imipramine: 335, LiCl: 210, ketamine: 325, MK801: 323 or haloperidol: 255 are shown. P-values were calculated by Wilcoxon Rank Sum test and adjusted with Benjamini–Hochberg procedure and are indicated as follows: *p-value ≤ 0.05; **p-value * ≤ 0.01; ***p-value ≤ 0.001; ****p-value ≤ 0.0001. (B) Mean distance, turning, pausing and spurting during the first 10 min following 100 mM NaCl was measured. The number of fish per group were as follows: control/E3 = 47, NaCl = 47. (C) Zebrafish behaviours during the 10 min following the 1 min startle period are shown with or without treatment with pharmacological inhibitors or activators of JNK and downstream signalling hubs. As above, drug treatments were for 1 h before exposure to the startle battery. Mean distance, turning, pausing, spurting, time and distance thigmotaxis are shown for the following numbers of fish measurements (from 5 cycles per zebrafish larva): JNK-IN-8: 360, SP600125: 224, haloperidol: 220, SB216763: 358, FR236924: 360, R18: 354, SC79: 318, BIM: 216, PMA: 115, SB590885: 206, bryostatin-1: 359, AKTi: 360. P-values were calculated by Wilcoxon Rank Sum test and adjusted with Benjamini–Hochberg procedure and are indicated as follows *p-value ≤ 0.05; **p-value * ≤ 0.01; ***p-value ≤ 0.001; ****p-value ≤ 0.0001.