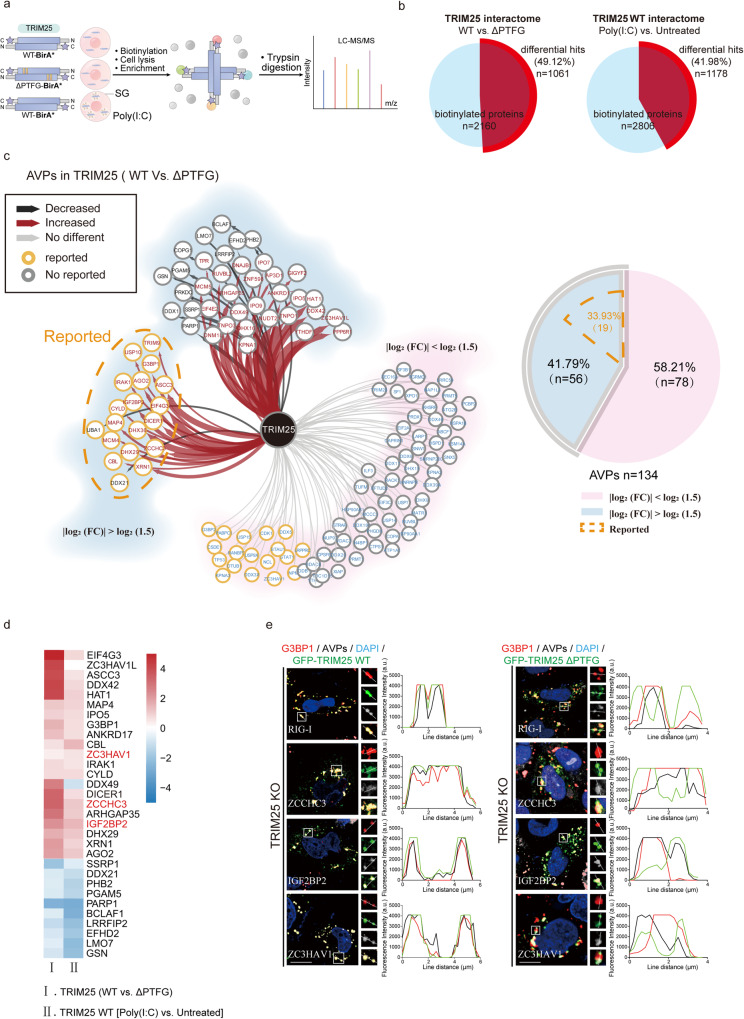
Fig. 4. Co-condensation with G3BP1 promotes TRIM25 to access SG-localized AVPs.
a Schematic depicting TRIM25 BioID methodology coupled to TMT-based quantitative proteomics. b Summary of comparison of TRIM25 WT vs. ∆PTFG or poly(I:C) vs. untreated proximal interactors. c TRIM25 WT vs. ∆PTFG differential proximal interactors from 134 AVPs. Cytoscape software was used to generate network (left) representing significance analysis of INTeractome (SAINT)-filtered putative TRIM25-prey differential interactions identified by BirA*. Each node represents a selected hit from the screen, organized by the presence or absence of differences, and the relationship between increases and decreases. Label those proteins that have been reported to synergize immunomodulation with TRIM25. Pie chart (right) is a broad generalization of the TRIM25 WT vs. ∆PTFG differential proximal interactors from AVPs. d Comparison of TRIM25 WT vs. ∆PTFG or TRIM25 WT poly(I:C) vs. untreated proximal interactors reveals a remarkable concordance in the change of AVPs. e Representative images of AVPs subcellular localization HeLa cells. Cells were transfected with GFP-TRIM25 WT or ∆PTFG and then treated with poly(I:C). DAPI staining is shown in blue. Line scans show the related intensity profiles of TRIM25, G3BP1 and AVPs. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments (e). Scale bars, 10 μm (e). (a.u. arbitrary units.).